Navigating the world of health insurance can feel like deciphering a complex code. The promise of “cheapest best health insurance” often seems elusive, a contradiction in terms. This guide unravels that apparent paradox, offering a practical understanding of how to find affordable yet comprehensive coverage. We’ll explore the factors influencing costs, unveil strategies for saving money, and empower you to make informed decisions about your health and financial well-being.
From understanding the nuances of different plan types (HMO, PPO, POS) to leveraging government subsidies and exploring cost-saving strategies, we provide a clear and concise path to securing the best possible health insurance without breaking the bank. We’ll equip you with the knowledge to compare plans effectively, understand crucial terminology, and ultimately, make a choice that aligns with your individual needs and budget.
Defining “Cheapest Best Health Insurance”
Finding the “cheapest best” health insurance is a common goal, but it presents a fundamental challenge. The terms “cheapest” and “best” are often at odds; what’s cheapest might lack crucial coverage, while the best coverage often comes with a higher price tag. Understanding this inherent conflict is key to making an informed decision.
Factors Affecting Health Insurance Costs
Several factors contribute to the overall cost of health insurance premiums. These include the insurer’s administrative costs, the healthcare provider’s rates (doctors, hospitals, specialists), the insured population’s health status (higher risk populations generally lead to higher premiums), and the level of coverage offered. Geographic location also plays a role; premiums tend to be higher in areas with a higher cost of living and greater demand for healthcare services. The type of plan chosen also significantly impacts the cost, with some plans offering more comprehensive coverage but charging higher premiums. Finally, government regulations and mandates, such as those requiring certain essential health benefits, can also influence costs.
Types of Health Insurance Plans and Cost Variations
Different types of health insurance plans offer varying levels of coverage and cost accordingly. Here are some common examples:
| Plan Type | Coverage | Premiums | Deductibles | Co-pays |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMO (Health Maintenance Organization) | Generally lower premiums, but requires using in-network providers. | Lower | Typically higher | Lower |
| PPO (Preferred Provider Organization) | Higher premiums, but allows using out-of-network providers (at a higher cost). | Higher | Typically lower | Higher |
| EPO (Exclusive Provider Organization) | Similar to HMO but with stricter rules on out-of-network care (usually no coverage). | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| POS (Point of Service) | Combines features of HMO and PPO, offering some flexibility with out-of-network care. | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
Note: The specific costs and coverage details for each plan type will vary depending on the insurer, location, and individual circumstances. These are general comparisons. For instance, a young, healthy individual might find a high-deductible plan more affordable, while an older person with pre-existing conditions might prefer a plan with lower out-of-pocket costs, even if it means higher premiums.
Factors Influencing Health Insurance Costs

Several key factors interact to determine the cost of health insurance premiums. Understanding these factors empowers consumers to make informed decisions and potentially reduce their expenses. This section will explore the significant influences on premium pricing, including personal characteristics and plan choices.
The Role of Age, Health Status, Location, and Family Size
Age is a significant factor in health insurance pricing. Older individuals generally require more medical care, leading to higher premiums. Pre-existing health conditions also play a crucial role. Individuals with chronic illnesses or a history of significant medical issues will typically face higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of future healthcare needs. Geographic location significantly impacts costs. Areas with higher healthcare provider costs or a greater concentration of specialists tend to have higher premiums. Finally, family size influences premiums, as larger families generally incur higher healthcare expenses. For example, a family with multiple children may have higher premiums than a single individual, reflecting the increased probability of needing pediatric care and other family-related services.
Employer-Sponsored vs. Individual Plans
Employer-sponsored health insurance plans often offer lower premiums than individual plans due to economies of scale and group purchasing power. Employers negotiate rates with insurance companies on behalf of their employees, resulting in potentially more favorable pricing. Individual plans, purchased directly from an insurance company, often lack these advantages and can be significantly more expensive. The extent of the cost difference varies depending on factors like the employer’s size, industry, and the specific plan offered. For example, a large corporation might secure significantly lower rates than a small business or an individual purchasing a plan on the marketplace.
Health Insurance Networks: HMO, PPO, POS
Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) typically offer the lowest premiums but have restrictive networks of providers. Individuals must choose a primary care physician (PCP) within the network who then refers them to specialists, also within the network. Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs) offer more flexibility, allowing individuals to see out-of-network providers, though at a higher cost. Point-of-Service (POS) plans combine features of both HMOs and PPOs, offering a balance between cost and choice. The choice between these plans depends heavily on individual needs and preferences regarding access to specialists and the willingness to pay more for increased flexibility. A person who prioritizes cost savings and has a limited need for specialized care might find an HMO suitable, while someone requiring frequent specialist visits might prefer a PPO despite the higher premiums.
Strategies for Reducing Health Insurance Costs
Understanding the factors that drive health insurance costs allows for proactive strategies to minimize expenses.
- Enroll during open enrollment: Missing the open enrollment period can lead to penalties or limited plan options.
- Consider a higher deductible plan: Higher deductibles generally translate to lower premiums, suitable for individuals with good health and a lower risk of frequent medical expenses.
- Explore employer-sponsored plans: Take advantage of employer-sponsored plans, which often offer more affordable options than individual plans.
- Compare plans carefully: Thoroughly compare plans from different insurers to find the best value for your needs and budget.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Preventative care and healthy habits can reduce the likelihood of needing expensive medical treatments in the future.
- Take advantage of preventive services: Many plans cover preventive services at no cost, helping to detect potential problems early and avoid more costly treatments later.
Finding Affordable Health Insurance Options
Securing affordable health insurance can feel daunting, but with the right resources and understanding, it’s achievable. This section Artikels key strategies, resources, and potential pitfalls to navigate the process successfully. We’ll explore ways to find suitable plans, understand potential cost-saving options, and avoid common mistakes.
Finding affordable health insurance involves leveraging various resources and understanding your options. This includes utilizing online comparison tools, exploring government subsidies, and carefully reviewing plan details to ensure a good fit for your individual needs and budget.
Resources for Finding and Comparing Health Insurance Plans
Several resources facilitate the search for and comparison of health insurance plans. These include government websites dedicated to health insurance marketplaces, and independent comparison websites that aggregate plan information from various insurers.
The Healthcare.gov website is a primary resource for finding plans offered through the Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplaces. It allows users to input their location, income, and family size to identify eligible plans and estimate potential subsidies. Many states also operate their own marketplaces, offering similar functionalities. Independent comparison websites, such as eHealthInsurance and HealthSherpa, provide a broader range of plans from various insurers, often simplifying the comparison process by allowing side-by-side analysis of benefits, premiums, and out-of-pocket costs. These sites often include tools to filter plans based on specific needs, such as preferred doctors or specific coverage requirements.
Potential Pitfalls to Avoid When Selecting a Health Insurance Plan
Choosing a health insurance plan requires careful consideration to avoid potential financial burdens. Failing to accurately assess your healthcare needs and neglecting to understand the plan’s specifics are common pitfalls. Overlooking the deductible, copay, and out-of-pocket maximum can lead to unexpected expenses. Furthermore, selecting a plan solely based on the lowest premium without considering the network of doctors and hospitals can restrict access to needed care. It’s crucial to compare plans based on their overall value, considering the balance between premiums, deductibles, co-pays, and the breadth of the provider network.
Government Subsidies and Programs Assisting with Health Insurance Affordability
Several government subsidies and programs aim to increase health insurance affordability. The most significant is the Affordable Care Act (ACA), which provides premium tax credits and cost-sharing reductions to individuals and families who meet specific income requirements. Medicaid, a joint federal and state program, provides healthcare coverage to low-income individuals and families, while CHIP (Children’s Health Insurance Program) covers uninsured children in families who earn too much to qualify for Medicaid but cannot afford private insurance.
Application Process for Government Assistance Programs
The application process for government assistance programs varies depending on the specific program and state. Generally, applications are submitted online through designated websites or via paper applications. Information required typically includes income, household size, and citizenship status.
| Program | Application Method | Website | Eligibility Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marketplace Subsidies (ACA) | Online through Healthcare.gov or state marketplace | Healthcare.gov (or state marketplace website) | Income-based; varies by state and household size |
| Medicaid | Online or paper application through state agency | State Medicaid agency website | Income and resource limits; varies by state |
| CHIP | Online or paper application through state agency | State CHIP agency website | Income limits; varies by state; for children under 19 |
Understanding Health Insurance Coverage
Choosing the “cheapest best” health insurance plan requires a thorough understanding of what that plan actually covers. Knowing the terminology and the specifics of your coverage is crucial to avoid unexpected medical bills and ensure you receive the care you need. This section clarifies key terms and concepts to help you navigate the complexities of health insurance policies.
Key Terms and Concepts in Health Insurance
Understanding the terminology is the first step to making informed decisions. Several key terms define your responsibilities and the insurance company’s responsibilities when it comes to covering medical expenses.
- Deductible: This is the amount you must pay out-of-pocket for covered healthcare services before your insurance company starts paying. For example, a $1,000 deductible means you’ll pay the first $1,000 of your medical bills before your insurance coverage kicks in.
- Copay: A copay is a fixed amount you pay for a covered healthcare service, such as a doctor’s visit. Copays are typically due at the time of service. For example, a $30 copay means you pay $30 each time you see your doctor.
- Coinsurance: After you’ve met your deductible, coinsurance is the percentage of the costs you’re responsible for. For example, an 80/20 coinsurance means your insurance company pays 80% of the costs, and you pay the remaining 20%.
- Out-of-Pocket Maximum: This is the most you will pay out-of-pocket for covered healthcare services in a plan year. Once you reach this limit, your insurance company pays 100% of the costs for covered services. For example, an out-of-pocket maximum of $5,000 means that once you’ve paid $5,000, your insurance company will cover all remaining expenses for the rest of the year.
Importance of Understanding Plan Specifics Before Enrollment
Failing to thoroughly review a plan’s details before enrolling can lead to significant financial burdens. Understanding your deductible, copay, coinsurance, and out-of-pocket maximum is vital for budgeting and managing healthcare expenses. Furthermore, knowing which doctors and hospitals are in-network is crucial for minimizing costs. Out-of-network care typically results in higher out-of-pocket expenses.
Coverage Comparison Across Different Plan Types
Different health insurance plans offer varying levels of coverage for various medical services. For instance, a Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) plan typically requires you to choose a primary care physician (PCP) who acts as a gatekeeper to specialists. In contrast, a Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) plan usually offers more flexibility in choosing doctors and specialists, but often at a higher cost. Point-of-Service (POS) plans combine elements of both HMOs and PPOs. Understanding these differences is key to selecting a plan that aligns with your healthcare needs and budget.
Sample Insurance Policy Coverage Details
Imagine a sample policy with a $2,000 deductible, a $30 copay for doctor visits, 80/20 coinsurance, and a $6,000 out-of-pocket maximum. This means that for the first $2,000 of medical expenses, you pay everything. After that, you pay 20% of the remaining costs until you reach $6,000. After you’ve paid $6,000, your insurance covers 100% of covered expenses for the rest of the year. However, this plan may exclude certain services, such as experimental treatments or cosmetic procedures, even after the out-of-pocket maximum is met. The plan might also have limitations on the number of specialist visits allowed per year. A detailed summary of benefits and exclusions would be included in the plan document. This illustrative example highlights the importance of reading the fine print to fully understand your coverage.
Maintaining Affordable Health Insurance

Securing affordable health insurance is a significant financial and personal goal. However, maintaining that affordability over time requires proactive strategies and a mindful approach to healthcare. Understanding the factors that influence your premiums and actively managing your health can significantly impact your long-term insurance costs.
Strategies for Maintaining Affordable Health Insurance
Several key strategies can help you keep your health insurance premiums manageable. These strategies involve a combination of financial planning, informed decision-making, and proactive health management. Consistent application of these strategies can lead to significant long-term savings.
- Regularly Review Your Coverage: Annually, compare plans available on the marketplace or through your employer. Changes in your health status, family size, or income may qualify you for subsidies or more affordable plans. Don’t assume your current plan is always the best option.
- Consider a High-Deductible Plan with a Health Savings Account (HSA): High-deductible plans typically have lower premiums. Coupled with an HSA, which allows tax-advantaged savings for healthcare expenses, this can be a cost-effective strategy for healthy individuals or those with predictable healthcare needs. Remember to contribute to your HSA regularly to maximize its benefits.
- Negotiate with Providers: Before receiving care, inquire about pricing and payment options. Many providers offer discounts for cash payments or payment plans. Shopping around for providers can also yield significant savings.
- Utilize Telemedicine: For non-emergency situations, telemedicine offers a convenient and often less expensive alternative to in-person visits. This is particularly useful for routine check-ups or follow-up appointments.
Impact of Lifestyle Choices on Health Insurance Costs
Your lifestyle significantly influences your health and, consequently, your insurance costs. Unhealthy habits can lead to increased medical expenses, which can result in higher premiums or even policy cancellations in some cases.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use: Smoking significantly increases the risk of numerous health problems, leading to higher insurance premiums. Many insurers charge substantially more for smokers than non-smokers.
- Obesity and Lack of Exercise: Obesity increases the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and other chronic conditions, all of which contribute to higher healthcare costs. Regular exercise and a balanced diet can mitigate these risks.
- Poor Diet: A diet lacking in essential nutrients can weaken the immune system and increase susceptibility to illness, leading to more frequent doctor visits and increased healthcare spending.
- Substance Abuse: Substance abuse significantly increases the risk of various health problems, resulting in higher healthcare costs and potentially impacting insurance eligibility.
Preventing Unnecessary Medical Expenses
Taking proactive steps to prevent unnecessary medical expenses can significantly reduce your healthcare costs over time. This includes focusing on preventative care and making informed decisions about your healthcare.
- Preventive Care: Regular check-ups, screenings, and vaccinations can help detect and address health issues early, preventing them from developing into more serious and costly problems.
- Medication Management: Properly managing your medications, including taking them as prescribed and understanding potential side effects, can prevent costly hospitalizations or emergency room visits.
- Understanding Your Insurance Coverage: Familiarize yourself with your plan’s benefits, deductibles, and co-pays to avoid unexpected expenses. Understanding your coverage helps you make informed decisions about your healthcare.
- Seeking Appropriate Care: Utilize urgent care clinics or telehealth services for non-emergency situations to avoid unnecessary emergency room visits, which are often significantly more expensive.
Preventative Care’s Impact on Long-Term Health Insurance Costs
Investing in preventative care is a long-term strategy that can substantially reduce your overall healthcare costs. Early detection and prevention of health issues are far less expensive than treating chronic conditions.
For example, regular screenings for conditions like high blood pressure or high cholesterol can allow for early intervention, preventing the development of more serious complications like heart disease or stroke, which require significantly more extensive and costly treatment. Similarly, routine dental check-ups can prevent minor dental problems from escalating into costly procedures. The cost of preventative care is minimal compared to the potential savings from avoiding costly treatments down the line. This translates to lower premiums and overall reduced healthcare burden.
Outcome Summary
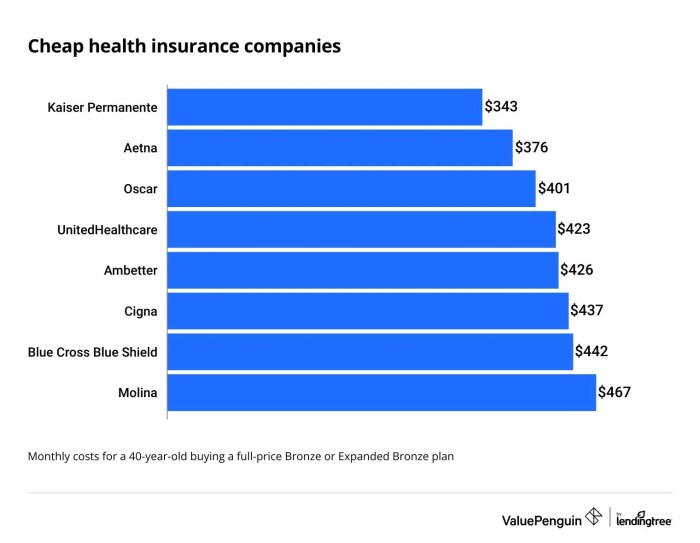
Securing the best and most affordable health insurance requires careful planning and a thorough understanding of your options. By weighing the factors discussed – from premium costs and deductibles to network limitations and coverage specifics – you can confidently select a plan that provides adequate protection without unnecessary financial strain. Remember, proactive health management and understanding your policy’s details are key to long-term affordability and peace of mind. Take control of your healthcare journey by making informed decisions based on the knowledge gained here.
Q&A
What is a deductible?
A deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket for covered healthcare services before your insurance coverage kicks in.
What is the difference between HMO and PPO plans?
HMOs typically require you to choose a primary care physician (PCP) who coordinates your care and referrals to specialists. PPOs offer more flexibility, allowing you to see specialists without a referral, but generally at a higher cost.
How can I reduce my health insurance costs?
Consider enrolling in a high-deductible plan with a health savings account (HSA), choosing a plan with a smaller network, and practicing preventative care to avoid costly medical issues.
Where can I find information about government subsidies?
Check the Healthcare.gov website (for US residents) or your country’s equivalent health insurance marketplace for information on subsidies and eligibility requirements.
What is a copay?
A copay is a fixed amount you pay for a covered healthcare service, such as a doctor’s visit, at the time of service.