
General liability insurance serves as a crucial safety net for businesses of all sizes, protecting against the financial repercussions of unforeseen accidents and incidents. From a small bakery to a large corporation, the potential for liability is ever-present. This guide delves into the intricacies of general liability insurance, providing a clear understanding of its coverage, limitations, and the process of obtaining and utilizing this vital protection.
We will explore the various aspects of general liability insurance, including its definition, the types of businesses that benefit from it, and the specific situations where coverage is provided. We’ll also examine the factors that influence premium costs and offer a step-by-step guide to purchasing a policy, along with advice on navigating the claims process. By the end, you’ll possess a robust understanding of how general liability insurance can safeguard your business’s future.
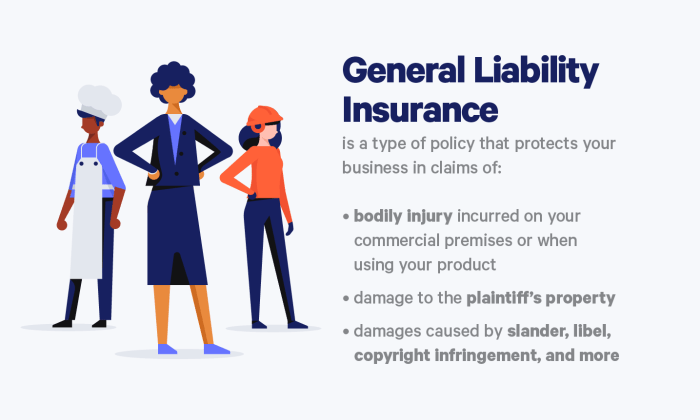
Definition and Scope of General Liability Insurance
General liability insurance is a crucial component of risk management for many businesses. It acts as a financial safety net, protecting businesses from the costs associated with third-party claims of bodily injury or property damage. Understanding its scope is essential for any business owner seeking to mitigate potential financial losses.
General liability insurance primarily covers claims arising from the business’s operations, not the business owner’s personal life. It protects against lawsuits alleging negligence or other incidents causing harm to others. This protection extends to various situations, offering peace of mind and financial security.
Types of Businesses Requiring General Liability Insurance
Many businesses benefit from having general liability insurance, regardless of size or industry. The need for this coverage stems from the inherent risks associated with operating a business and interacting with the public. For example, a small retail store faces the risk of a customer slipping and falling, while a larger manufacturing company might face claims related to product defects. The broader the potential for interaction with the public and the higher the potential for accidents, the more critical general liability insurance becomes. Therefore, a wide range of businesses, from restaurants and retailers to construction companies and professional service providers, typically require this coverage.
Examples of Situations Covered by General Liability Insurance
General liability insurance provides protection against a wide range of situations. For instance, if a customer is injured on a business’s premises due to a hazard like a wet floor, the insurance policy could cover medical expenses and legal costs associated with a resulting lawsuit. Similarly, if a business’s product causes damage to a customer’s property, the insurance can help cover the costs of repair or replacement. Another example is advertising injury, where a business is sued for libel or slander in its advertising materials. These are just a few scenarios where general liability insurance offers crucial protection.
Comparison of General Liability Insurance with Other Business Insurance Types
The following table compares general liability insurance with other common types of business insurance, highlighting their key differences and the specific risks each covers.
| Insurance Type | Coverage | Typical Claims | Who Needs It? |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Liability | Bodily injury or property damage caused by the business to third parties. | Slip and fall accidents, product liability, advertising injury. | Most businesses interacting with the public or having premises open to the public. |
| Professional Liability (Errors & Omissions) | Negligent acts, errors, or omissions in professional services. | Medical malpractice, accounting errors, architectural design flaws. | Professionals offering advice or services (doctors, lawyers, consultants). |
| Workers’ Compensation | Medical expenses and lost wages for employees injured on the job. | Workplace accidents, injuries resulting from work-related activities. | Businesses with employees. |
| Commercial Auto | Damage or injury caused by company vehicles. | Accidents involving company cars, trucks, or other vehicles. | Businesses that own or operate vehicles for business purposes. |
Coverage Provided by General Liability Insurance
General liability insurance provides crucial protection for businesses and individuals against financial losses arising from third-party claims of bodily injury or property damage caused by their operations or negligence. Understanding the key components of this coverage is vital for effective risk management. This section details the specific types of claims typically covered under a standard general liability policy.
Bodily Injury Claims
Bodily injury claims encompass a wide range of situations resulting in physical harm to another person. These claims can stem from various incidents, leading to significant financial repercussions for the insured if not covered by insurance. Examples include injuries sustained on business premises, injuries caused by a product manufactured or sold by the insured, or injuries resulting from the negligence of the insured’s employees.
- A customer slips and falls on a wet floor in a store, resulting in a broken leg.
- A delivery driver, while making a delivery, accidentally backs into a pedestrian, causing injuries.
- A defective product manufactured by a company causes injury to a consumer.
Property Damage Claims
Property damage claims involve incidents where the insured’s actions or negligence result in damage to the property of another. These claims can range from minor damage to extensive destruction, resulting in substantial financial liability. It’s important to note that property damage coverage typically excludes damage to the insured’s own property.
- A contractor accidentally damages a client’s building during renovations.
- A fire originating from the insured’s premises spreads to a neighboring building.
- A company’s delivery truck accidentally collides with another vehicle, causing damage to the other vehicle.
Advertising Injury Claims
Advertising injury coverage protects businesses against claims arising from their advertising activities. This often involves allegations of libel, slander, or infringement of copyright or other intellectual property rights. These claims can severely impact a company’s reputation and financial stability.
- A company’s advertisement falsely accuses a competitor of unethical practices, leading to a defamation lawsuit.
- A company uses another company’s logo without permission in its advertising materials, resulting in an infringement claim.
- An advertisement contains inaccurate information about a product, leading to a claim of misrepresentation.
Exclusions and Limitations of General Liability Insurance

General liability insurance, while offering crucial protection for businesses, doesn’t cover every conceivable risk. Understanding the exclusions and limitations within your policy is vital to avoid costly surprises when filing a claim. This section details common exclusions and explains how policy limits affect coverage.
Common Exclusions in General Liability Policies
It’s important to carefully review your specific policy wording, as exclusions can vary between insurers and policy types. However, some common exclusions frequently appear in general liability insurance contracts. These exclusions limit the scope of coverage and are designed to manage risk for the insurance company.
- Expected or Intended Injury: This exclusion prevents coverage for injuries or damages that the insured intentionally caused. For example, if a business owner deliberately assaults a customer, the policy won’t cover the resulting legal liabilities.
- Contractual Liability: Generally, general liability insurance won’t cover liabilities stemming from contractual agreements unless specifically included as an endorsement. This often involves situations where the insured assumed liability through a contract.
- Pollution or Environmental Damage: Most policies exclude coverage for pollution or environmental contamination, unless specifically added as an endorsement. This typically excludes cleanup costs and liabilities associated with environmental hazards.
- Liquor Liability: Unless a specific endorsement is added, general liability insurance usually excludes liability arising from the sale, distribution, or serving of alcoholic beverages. This is often a separate coverage needing its own policy.
- Professional Services: Errors or omissions in professional services, such as those provided by doctors, lawyers, or consultants, are typically excluded from general liability policies and require separate professional liability insurance.
- Workers’ Compensation: Injuries to employees are covered under workers’ compensation insurance, not general liability. Attempting to use general liability for employee injuries will likely result in claim denial.
- Automobile Accidents: Damages arising from automobile accidents are usually covered under auto insurance, not general liability. This exclusion applies even if the accident occurs on the insured’s premises.
Policy Limits and Their Implications
General liability policies have limits, expressed as dollar amounts, representing the maximum the insurer will pay for covered losses. These limits are usually stated as per occurrence and aggregate limits. A “per occurrence” limit refers to the maximum payout for a single incident, while the “aggregate” limit is the maximum payout for all incidents during the policy period. Exceeding these limits leaves the insured responsible for any remaining costs.
For example, a policy with a $1 million per occurrence limit and a $2 million aggregate limit would pay a maximum of $1 million for any single incident, even if multiple claims arise from that incident. The total payout for all incidents during the policy year cannot exceed $2 million.
Examples of Claim Denials
Several scenarios illustrate situations where a claim would likely be denied:
A business owner intentionally damages a competitor’s property during a dispute. This falls under the “expected or intended injury” exclusion.
A contractor fails to complete a project as agreed upon in a contract, leading to financial losses for the client. This may fall under the “contractual liability” exclusion unless specifically covered.
A manufacturing plant releases toxic chemicals into a nearby river, causing environmental damage. This is likely excluded under “pollution or environmental damage.”
Factors Affecting General Liability Insurance Premiums
The cost of general liability insurance is not a fixed amount; it varies significantly depending on several interconnected factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses to effectively manage their risk and budget for insurance costs. This section will explore the key elements that influence premium calculations.
Business Size and Industry
Business size directly impacts premium costs. Larger businesses, with more employees and extensive operations, generally face higher premiums due to the increased potential for incidents and resulting liability claims. The complexity of their operations and the number of potential exposure points contribute to this increased risk. Similarly, the industry in which a business operates plays a significant role. High-risk industries, such as construction or manufacturing, tend to have higher premiums than lower-risk industries, like retail or office administration. This difference reflects the inherent hazards associated with each sector. For instance, a construction company faces a higher likelihood of accidents and injuries compared to a bookstore. The inherent dangers of the work environment directly translate into higher insurance premiums.
Risk Assessment and Loss History
Insurers meticulously assess the risk profile of each business before setting premiums. This involves examining factors like the business’s safety record, past claims history, and the nature of its operations. A business with a history of accidents or significant liability claims will likely face higher premiums as it demonstrates a higher risk profile. Conversely, a business with a strong safety record and no prior claims will typically receive more favorable rates. This reflects the insurer’s assessment of the likelihood of future claims. For example, a manufacturing plant with a documented history of workplace injuries would expect higher premiums compared to a similar plant with a strong safety program and no reported incidents.
Location
The geographical location of a business also affects its general liability insurance premiums. Areas with higher crime rates, more frequent natural disasters, or stricter regulatory environments often command higher premiums. Insurers consider the likelihood of incidents and the potential severity of losses in a given location. A business operating in a high-crime area might face higher premiums due to the increased risk of theft or vandalism, while a business located in an area prone to earthquakes or hurricanes might face higher premiums to account for potential property damage and liability claims. The location’s risk profile, as determined by statistical data and historical claims, directly influences the premium.
Hypothetical Scenario: Premium Calculation Differences
Consider two businesses: “Acme Construction,” a large construction firm with a history of workplace accidents, operating in a high-risk area prone to severe weather; and “Beta Books,” a small bookstore with a spotless safety record located in a low-crime, low-risk area. Acme Construction would undoubtedly face significantly higher premiums than Beta Books due to its size, industry, accident history, and location. The combination of these factors leads to a higher perceived risk, resulting in a substantially higher insurance cost. The premium difference could be several times higher, reflecting the disparity in risk profiles.
Illustrative Scenarios

Understanding how general liability insurance works in practice is best achieved through real-world examples. The following scenarios illustrate common situations where this type of insurance provides crucial protection.
Bodily Injury Claim Scenario
A catering company, “Delicious Delights,” was hired for a large corporate event. During the event, a waiter carrying a tray of hot coffee tripped and spilled the coffee on a guest, causing second-degree burns. The guest, Mr. Jones, incurred significant medical expenses and lost wages due to his injuries. He filed a claim against Delicious Delights for his medical bills, lost wages, and pain and suffering. Delicious Delights, holding a general liability insurance policy with a $1 million liability limit, reported the incident to their insurer. The insurance company investigated the claim, gathering evidence including medical records, witness statements, and photographs of Mr. Jones’s injuries. After negotiations, the insurance company settled the claim with Mr. Jones for $75,000, covering his medical expenses and a portion of his lost wages and pain and suffering. The settlement amount remained well within the policy’s limit, preventing Delicious Delights from incurring significant out-of-pocket expenses.
Property Damage Claim Scenario
A contractor, “BuildRight Construction,” was renovating a commercial building. During demolition work, a section of the building’s wall unexpectedly collapsed, damaging a neighboring property’s fence and causing minor damage to a parked car. The owner of the neighboring property, Ms. Smith, filed a claim against BuildRight Construction for the cost of repairing her fence and the damage to the car. BuildRight Construction, insured under a general liability policy with a $500,000 liability limit, notified their insurer. The insurance company investigated, assessing the damage to the fence and the car with independent estimators. They also reviewed the contractor’s work permits and safety procedures. The insurer settled the claim with Ms. Smith for $20,000, covering the repair costs for the fence and the car damage. The settlement amount was significantly less than the policy limit, protecting BuildRight Construction from substantial financial losses.
Wrap-Up
Securing adequate general liability insurance is a proactive step that demonstrates responsible business management. Understanding the scope of coverage, potential exclusions, and the claims process empowers businesses to make informed decisions and mitigate financial risks. By carefully considering the factors that influence premiums and selecting a reputable insurer, businesses can confidently navigate the complexities of liability protection and focus on their core operations knowing they are adequately protected against unforeseen circumstances.
Common Queries
What types of businesses need general liability insurance?
Virtually any business that interacts with the public or third parties should consider general liability insurance, regardless of size. This includes, but is not limited to, retailers, restaurants, contractors, and service providers.
How much does general liability insurance cost?
The cost varies greatly depending on factors such as business type, location, size, and claims history. It’s best to obtain quotes from multiple insurers to compare pricing.
What if my claim is denied?
If your claim is denied, you have the right to appeal the decision. Review your policy carefully and gather all relevant documentation to support your appeal. You may also want to consult with an attorney.
Can I get general liability insurance if I have a poor claims history?
While a poor claims history may lead to higher premiums, it doesn’t necessarily preclude you from obtaining coverage. Be upfront about your past claims when applying for insurance.
What is the difference between general liability and professional liability insurance?
General liability covers bodily injury or property damage caused by your business operations. Professional liability (errors and omissions insurance) covers claims of negligence or mistakes in professional services provided.