
Securing affordable home owners insurance shouldn’t feel like navigating a maze. This comprehensive guide demystifies the process, offering practical strategies and insights to help you find the best coverage at a price that fits your budget. We’ll explore the factors influencing insurance costs, effective ways to lower premiums, and the crucial steps to securing a policy that provides peace of mind without breaking the bank.
From understanding policy intricacies to leveraging discounts and negotiating with insurers, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions. This isn’t just about finding the cheapest option; it’s about finding the right balance between cost and comprehensive protection for your most valuable asset – your home.
Understanding “Cheap Homeowners Insurance”
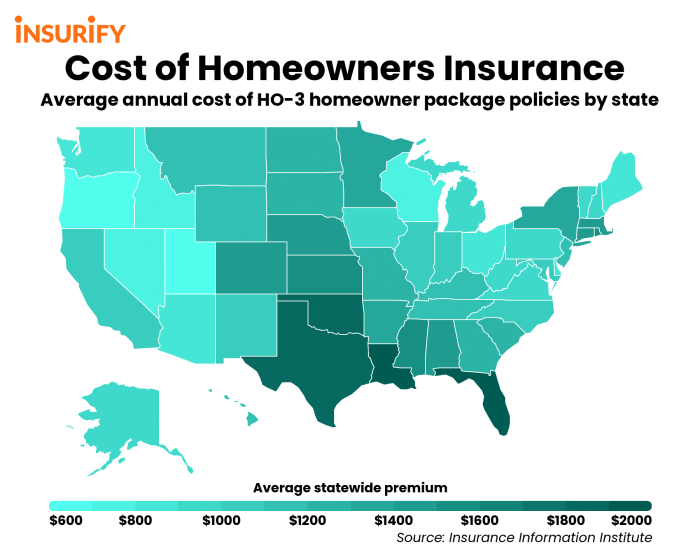
Finding affordable homeowners insurance is a priority for many, but “cheap” shouldn’t mean inadequate coverage. Understanding the factors that influence cost and the nuances of different policies is crucial to securing the right balance of price and protection. This section will clarify the key aspects of homeowners insurance pricing and coverage.
Factors Influencing Homeowners Insurance Cost
Several factors significantly impact the premium you’ll pay for homeowners insurance. These factors are carefully assessed by insurance companies to determine your risk profile. A higher-risk profile generally translates to a higher premium.
- Location: Your home’s location plays a major role. Areas prone to natural disasters like hurricanes, earthquakes, wildfires, or floods will command higher premiums due to increased risk. For example, a home in a coastal area susceptible to hurricanes will typically cost more to insure than a similar home in a less disaster-prone inland location.
- Home Value: The higher the value of your home, the more expensive the insurance will be. This is because the insurer’s potential payout in case of damage is higher.
- Coverage Amount: The amount of coverage you choose directly impacts your premium. Higher coverage levels mean higher premiums, but also greater protection in the event of a significant loss.
- Deductible: Your deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Choosing a higher deductible will lower your premium, but you’ll have to pay more in the event of a claim.
- Credit Score: In many states, your credit score is a factor in determining your insurance premium. A good credit score often translates to lower premiums, reflecting a lower perceived risk.
- Home Features: Features like security systems, fire alarms, and updated plumbing and electrical systems can lower your premium, as they mitigate risk.
- Claims History: Your past claims history significantly influences your premium. Filing multiple claims can lead to higher premiums in the future.
Types of Homeowners Insurance Coverage
Homeowners insurance policies are categorized into different types, each offering varying levels of protection. Understanding these differences is essential in choosing the right coverage for your needs and budget.
- HO-3 (Special Form): This is the most common type, offering broad coverage for damage to your home and personal belongings. It covers a wide range of perils, except those specifically excluded.
- HO-5 (Comprehensive Form): Provides even broader coverage than HO-3, offering open-peril coverage for both your home and personal belongings. This means it covers damage from almost any cause, unless explicitly excluded.
- HO-4 (Renters Insurance): This policy protects your personal belongings if you rent your home. It does not cover the structure itself.
- HO-6 (Condominium Insurance): Designed for condominium owners, this policy covers your personal belongings and the interior of your unit, but typically excludes the building’s structure.
Common Exclusions in Homeowners Insurance Policies
While homeowners insurance provides comprehensive coverage, there are specific events or circumstances that are typically excluded. Understanding these exclusions is crucial to avoid surprises.
- Floods: Flood damage is usually excluded and requires separate flood insurance.
- Earthquakes: Earthquake damage often requires a separate policy.
- Intentional Acts: Damage caused intentionally by the homeowner is typically not covered.
- Normal Wear and Tear: Gradual deterioration of your home due to age is not covered.
- Neglect: Damage resulting from neglecting necessary repairs is usually excluded.
Pricing Structures of Various Insurance Providers
Insurance providers utilize different pricing models and algorithms to determine premiums. While specific pricing details are proprietary, some general observations can be made.
Large national insurers often have established pricing structures based on extensive data analysis. Smaller, regional companies may offer more competitive rates in specific areas, but their coverage options might be more limited. Online insurers frequently use technology to streamline the process and potentially offer lower premiums, although the level of customer service may vary. It’s essential to compare quotes from multiple providers to find the best value for your needs.
Finding Affordable Homeowners Insurance
Securing affordable homeowners insurance is crucial for protecting your most valuable asset. The cost of premiums can vary significantly depending on several factors, making it essential to understand how to navigate the insurance market effectively and find the best coverage at a price that fits your budget. This section will explore strategies to reduce premiums, guide you through comparing quotes, and highlight the importance of accurately assessing your home’s value.
Strategies for Reducing Homeowners Insurance Premiums
Several proactive steps can significantly impact your homeowners insurance premiums. Implementing these strategies can lead to considerable savings over the life of your policy.
- Improve your home’s security: Installing security systems, including alarms and monitored systems, often qualifies for discounts. These systems deter burglars and reduce the insurer’s risk.
- Upgrade your home’s safety features: Smoke detectors, fire sprinklers, and updated electrical systems can lower premiums by mitigating potential fire damage and other hazards. Consider replacing outdated plumbing to minimize water damage risks.
- Increase your deductible: Choosing a higher deductible will lower your monthly premium, but remember this means you’ll pay more out-of-pocket in the event of a claim. Carefully weigh the cost savings against your financial capacity to handle a larger deductible.
- Bundle your insurance policies: Many insurers offer discounts for bundling homeowners insurance with other policies, such as auto or umbrella insurance. This can create significant savings.
- Maintain a good credit score: Your credit history is a factor in determining your insurance rates. A good credit score demonstrates financial responsibility, which can lead to lower premiums.
- Shop around and compare quotes: Don’t settle for the first quote you receive. Comparing quotes from multiple insurers is essential to finding the best rates for your needs.
Checklist for Comparing Homeowners Insurance Quotes
Before committing to a policy, meticulously compare quotes using a structured checklist to ensure you’re making an informed decision. This approach avoids overlooking crucial details and helps secure the most suitable and affordable coverage.
- Coverage amounts: Verify the coverage amounts for dwelling, personal property, liability, and additional living expenses.
- Deductibles: Compare deductibles and their impact on premiums.
- Premiums: Note the annual and monthly premiums for each quote.
- Discounts: Check for available discounts (security systems, bundling, etc.).
- Policy features: Review policy inclusions and exclusions.
- Company reputation and financial stability: Research the insurer’s financial strength and customer reviews.
- Claims process: Understand the insurer’s claims process and customer service reputation.
Step-by-Step Guide to Obtaining Homeowners Insurance Quotes Online
Obtaining homeowners insurance quotes online is convenient and efficient. Follow these steps for a streamlined process.
- Gather necessary information: Prepare information about your home (address, square footage, year built, features), personal information, and desired coverage amounts.
- Visit multiple insurer websites: Use comparison websites or directly visit the websites of various insurance providers.
- Complete online quote forms: Accurately fill out the online quote forms, providing all requested information.
- Review and compare quotes: Carefully review the quotes received, paying close attention to the details mentioned in the checklist above.
- Contact insurers for clarification: If you have any questions or need clarification, contact the insurers directly.
- Choose a policy and purchase: Once you’ve selected the best policy, complete the purchase process online.
Understanding Your Home’s Value for Insurance Purposes
Accurately assessing your home’s value is paramount for securing adequate insurance coverage. Underinsuring your home can leave you financially vulnerable in the event of a significant loss.
Accurate valuation ensures you receive sufficient compensation to rebuild or repair your home in case of damage or destruction.
Determining your home’s value involves considering its replacement cost, which is often higher than its market value. Factors such as construction costs, materials used, and local market conditions all play a role. Consider consulting a professional appraiser for a precise valuation, especially for older homes or those with unique features. Using outdated or underestimated values can result in insufficient coverage and significant financial repercussions in the event of a claim.
Factors Affecting Insurance Costs
Several key factors influence the price of homeowners insurance. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions to potentially lower your premiums. Insurance companies use a complex algorithm considering various aspects of your property and personal circumstances.
Location
Your home’s location significantly impacts your insurance cost. Areas prone to natural disasters, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, wildfires, or floods, command higher premiums due to the increased risk for insurers. For example, a home situated in a coastal area with a high hurricane risk will typically have a substantially higher premium than a similar home in a less vulnerable inland location. Furthermore, the crime rate in your neighborhood also plays a role; higher crime rates generally lead to higher premiums.
Age and Condition of the Home
The age and condition of your home are crucial factors. Older homes, especially those lacking updated safety features, are often considered riskier and therefore more expensive to insure. Outdated electrical systems, plumbing, or roofing materials increase the likelihood of claims, driving up premiums. Conversely, well-maintained homes with recent upgrades often qualify for lower premiums. For instance, a home with a recently replaced roof will likely receive a better rate than one with a severely damaged or aging roof.
Credit Score
Surprisingly, your credit score can significantly influence your homeowners insurance premium. Insurers often view a lower credit score as an indicator of higher risk. This is based on the statistical correlation between credit history and claims behavior. While not universally applied, many insurers use credit-based insurance scores to assess risk and set premiums. Improving your credit score can potentially lead to lower insurance costs.
Home Security Features
Installing home security features can demonstrably lower your insurance premiums. Features like security systems (including monitored systems), smoke detectors, and fire suppression systems significantly reduce the risk of theft and property damage. Insurers often offer discounts for homeowners who have these safety measures in place. A monitored security system, for instance, can lead to a discount of up to 20% in some cases.
Impact of Home Features on Insurance Costs
The following table compares the cost impact of various home features:
| Feature | Impact on Premium | Example | Potential Discount (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security System (Monitored) | Reduces | ADT, Vivint, SimpliSafe | 5-20 |
| Updated Plumbing | Reduces | Replacing old galvanized pipes with PEX | 2-5 |
| New Roof (Impact-resistant shingles) | Reduces | Architectural shingles, tile | 5-15 |
| Fire Suppression System | Reduces | Sprinkler system | 10-20 |
Claims History
Your claims history significantly affects future insurance premiums. Filing multiple claims, especially for preventable incidents, can result in higher premiums or even policy cancellation. Insurers view frequent claims as indicators of higher risk. For example, consistently filing claims for minor water damage might lead to a significant premium increase. Conversely, a clean claims history often results in lower premiums and better rates from insurers. Maintaining a good claims history is crucial for securing affordable homeowners insurance.
Bundling and Discounts
Saving money on homeowners insurance often involves more than just finding the lowest initial premium. Strategic bundling and leveraging available discounts can significantly reduce your overall cost. Understanding these options and how to access them is crucial for securing the best possible rate.
Bundling homeowners insurance with other insurance policies, primarily auto insurance, is a common and effective way to lower premiums. Insurance companies often offer substantial discounts for customers who bundle their policies. This is because managing multiple policies for a single customer simplifies administrative processes and reduces the company’s overall risk. The savings generated through this efficiency are often passed on to the policyholder in the form of lower premiums.
Bundling Benefits
Bundling your homeowners and auto insurance with the same provider often results in a substantial discount, typically ranging from 10% to 25% or even more depending on the insurer and specific policies. This discount is applied to the total premium for both policies, making it a significant cost savings over purchasing them separately. For example, a homeowner paying $1200 annually for homeowners insurance and $800 annually for auto insurance might see a combined discount of 15%, saving them approximately $300 per year. This represents a considerable return on the simple act of bundling policies.
Common Discounts
Insurance companies offer a wide variety of discounts to incentivize responsible behavior and attract new customers. These discounts can significantly reduce your premium, sometimes by a considerable amount.
Discount Eligibility and Application
Securing discounts typically involves providing the necessary documentation to your insurance provider. For example, to claim a discount for a security system, you’ll need to provide proof of installation and a description of the system’s features. Similarly, discounts for multiple policies require providing policy numbers for all bundled insurance products. The application process generally involves contacting your insurance company either through their website, phone, or in person. They will guide you through the necessary steps to verify your eligibility and apply the discounts to your policy. It’s important to regularly review your policy and inquire about available discounts, as offerings can change over time. Many insurers proactively identify and apply discounts when appropriate, but it is always beneficial to confirm and be aware of all available options.
Policy Coverage and Deductibles
Understanding your homeowners insurance policy’s coverage and deductible is crucial for managing both your risk and your costs. The level of coverage you choose directly impacts your premium, while the deductible affects your out-of-pocket expenses in the event of a claim. Choosing the right balance between these two factors is key to finding affordable and adequate protection.
Choosing the right coverage level involves balancing the cost of premiums against the potential for significant losses. Higher coverage limits generally mean higher premiums, but offer greater financial protection in case of a major event like a fire or severe weather damage. Conversely, lower coverage limits translate to lower premiums but leave you more exposed financially if a significant loss occurs. It’s essential to assess your property’s value and your personal risk tolerance to determine the appropriate level of coverage.
Deductible’s Role in Managing Insurance Costs
The deductible is the amount you agree to pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. A higher deductible results in lower premiums because the insurance company’s risk is reduced. Conversely, a lower deductible means higher premiums, but you’ll pay less out-of-pocket if you file a claim. The optimal deductible depends on your financial situation and risk tolerance. For example, someone with a substantial emergency fund might opt for a higher deductible to save on premiums, while someone with limited savings might prefer a lower deductible to minimize out-of-pocket costs in case of an incident.
High vs. Low Deductibles: Premium and Out-of-Pocket Expense Comparison
Let’s illustrate the impact of deductible choices with a hypothetical example. Consider two homeowners with similar properties and risk profiles. Homeowner A chooses a $1,000 deductible, while Homeowner B chooses a $5,000 deductible. Homeowner A will likely pay higher premiums than Homeowner B. However, if a $2,000 claim arises, Homeowner A would pay $1,000 (the deductible) and the insurance company would cover the remaining $1,000. Homeowner B, on the other hand, would pay nothing as their claim is below their deductible. But if a $6,000 claim occurred, Homeowner A would only pay $1,000, while Homeowner B would pay $5,000. This example highlights the trade-off between premium costs and out-of-pocket expenses associated with different deductible levels.
Common Coverages in a Standard Homeowners Insurance Policy
Understanding the typical components of a standard policy is vital for making informed decisions. Below is a list of common coverage types:
- Dwelling Coverage: Protects the physical structure of your home.
- Other Structures Coverage: Covers detached structures like garages, sheds, or fences.
- Personal Property Coverage: Protects your belongings inside and outside your home.
- Loss of Use Coverage: Covers additional living expenses if your home becomes uninhabitable due to a covered event.
- Personal Liability Coverage: Protects you from lawsuits if someone is injured on your property.
- Medical Payments Coverage: Covers medical expenses for others injured on your property, regardless of fault.
It is important to note that specific coverage amounts and details can vary significantly between policies and insurance providers. It’s always recommended to carefully review your policy documents to fully understand your coverage.
Concluding Remarks

Finding cheap home owners insurance is achievable with careful planning and informed decision-making. By understanding the factors that influence premiums, utilizing available discounts, and comparing quotes effectively, you can secure a policy that offers the necessary coverage without compromising your financial stability. Remember, protecting your home is paramount, and this guide provides the tools to do so wisely and affordably.
Clarifying Questions
What is the difference between actual cash value (ACV) and replacement cost coverage?
ACV coverage pays for the depreciated value of your damaged property, while replacement cost coverage pays for the cost of replacing it with new materials, regardless of age.
How does my credit score affect my home insurance premiums?
Many insurers use credit scores as an indicator of risk. A higher credit score generally leads to lower premiums.
Can I get homeowners insurance if I have a previous claim?
Yes, but a previous claim might result in higher premiums. Be upfront about your claims history when applying for insurance.
What is a rider or endorsement in a homeowners insurance policy?
A rider or endorsement adds specific coverage to your existing policy, such as flood insurance or jewelry coverage, often for an additional premium.
How often should I review my homeowners insurance policy?
It’s recommended to review your policy annually, or whenever there are significant changes to your home or circumstances, to ensure it still adequately protects your needs.