
Navigating the complex world of business insurance can be daunting, particularly when understanding the nuances of liability coverage. This guide delves into the specifics of ACORD liability insurance, a crucial element for businesses seeking to protect themselves against financial losses stemming from potential incidents. We will explore the various ACORD forms, coverage limits, claims processes, and legal considerations to provide a clear and comprehensive understanding of this essential insurance type.
From defining the core components of ACORD liability insurance policies to examining the roles of insurers and brokers, this resource aims to equip businesses with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions about their liability protection. We will cover the different types of liability covered, common exclusions, risk mitigation strategies, and the steps involved in filing a claim, offering practical advice and real-world examples throughout.
Defining Acord Liability Insurance
Acord liability insurance isn’t a specific type of insurance itself, but rather a standardized set of forms used to document and transfer liability information between insurance companies and their clients. These forms, developed by the American Association of Insurance Services (AAIS), now known as Acord, streamline the process of obtaining and managing liability insurance coverage. Understanding these forms is crucial for businesses seeking appropriate liability protection.
Acord forms provide a consistent framework for describing the risks a business faces and the coverage it needs. This standardized approach makes it easier for insurers to assess risk and provide quotes, and it simplifies the claims process should an incident occur. The core function of Acord liability forms is to clearly and comprehensively document the insured’s liability exposures and the terms of their coverage.
Core Components of Acord Liability Insurance Policies
Acord liability forms typically include details such as the insured’s identity, the coverage period, the limits of liability, the types of liability covered, and any exclusions or limitations. They also often specify the policy’s deductible and the process for submitting a claim. The specific information required varies depending on the type of liability insurance being documented. Accurate completion of these forms is essential for securing appropriate coverage and avoiding potential disputes later.
Types of Liability Covered Under Acord Forms
Several types of liability are commonly addressed within Acord forms. These include general liability, which covers bodily injury or property damage caused by the insured’s business operations; professional liability (errors and omissions), protecting against claims of negligence or mistakes in professional services; and product liability, which covers claims arising from defects in products manufactured or sold by the insured. Other types, like auto liability or workers’ compensation, may also be documented using Acord forms, depending on the specific needs of the business.
Businesses Commonly Utilizing Acord Liability Insurance
A wide range of businesses use Acord forms to document their liability insurance. This includes small businesses, such as restaurants, retail stores, and consulting firms; larger corporations, encompassing manufacturers, contractors, and technology companies; and even non-profit organizations. Essentially, any business facing potential liability risks benefits from using Acord forms to clearly Artikel their coverage. The standardized format ensures clarity and consistency across various insurers and simplifies the insurance process for all involved parties.
Comparison of Acord Liability Insurance with Other Liability Insurance Types
It’s crucial to understand that Acord forms themselves aren’t a type of insurance but rather a tool for documenting insurance policies. Therefore, comparing “Acord liability insurance” to other types of liability insurance is inaccurate. Instead, the comparison should focus on the *types of liability coverage* documented via Acord forms, such as general liability, professional liability, or product liability, against the same types of coverage obtained through other means. The primary difference lies in the standardized format and streamlined process offered by Acord forms. While the underlying coverage remains the same, Acord forms provide a standardized and efficient way to document and manage that coverage.
Acord Forms and Their Applications
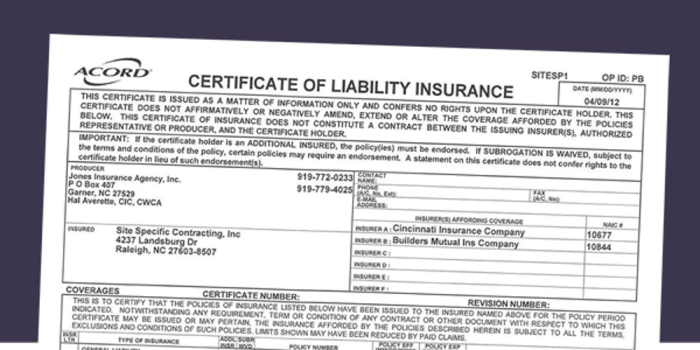
Acord forms are standardized documents used in the insurance industry to collect information necessary for underwriting and policy administration. Their consistent format streamlines the process for both insurers and insureds, ensuring all relevant data is captured efficiently and accurately. Understanding the most commonly used Acord forms and their applications is crucial for navigating the insurance landscape effectively.
Frequently Used Acord Forms
Several Acord forms are frequently used in liability insurance, each designed to gather specific details. These forms ensure consistent data collection, reducing ambiguity and improving the underwriting process. The information requested varies depending on the type of insurance and the specific needs of the insurer.
Information Required for Common Acord Forms
The information required on Acord forms varies depending on the specific form. However, common elements include the insured’s name and address, the nature of their business, the types of liability coverage sought, and details about their operations and risk profile. For example, Acord 25 requires detailed information about the insured’s operations, including the number of employees, the types of equipment used, and the locations where they operate. This information helps underwriters assess the risk involved and determine appropriate premiums. Similarly, Acord 28 provides a standardized method for reporting claims, facilitating efficient claim processing and resolution.
Best Practices for Completing Acord Forms
Accurate and efficient completion of Acord forms is essential for obtaining timely and appropriate insurance coverage. Carefully review each section of the form, ensuring all questions are answered completely and accurately. Use clear and concise language, avoiding jargon or ambiguous statements. If unsure about a particular question, contact your insurance broker or agent for clarification. Maintain organized records of completed forms, including supporting documentation, to facilitate future reference. Finally, review the completed form thoroughly before submission to ensure accuracy and completeness.
Comparison of Common Acord Forms
The following table compares several common Acord forms used in liability insurance, highlighting their key differences and applications.
| Acord Form | Purpose | Key Information Required | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acord 25 (Application for Liability Insurance) | To gather information about the applicant’s business and operations for underwriting purposes. | Business description, operations details, loss history, financials. | General liability, professional liability, commercial auto. |
| Acord 28 (Application for Workers’ Compensation Insurance) | To obtain information related to an applicant’s workers’ compensation insurance needs. | Payroll information, employee classifications, safety programs. | Workers’ compensation insurance. |
| Acord 130 (Application for Umbrella Liability Insurance) | To gather information for underwriting umbrella liability insurance policies. | Existing underlying liability insurance policies, loss history, assets. | Excess liability coverage. |
| Acord 24 (General Liability Supplemental Application) | To provide additional information related to general liability exposures. | Specific details on operations, hazardous materials, and other liability risks. | General liability insurance. |
Understanding Coverage Limits and Exclusions
Understanding the coverage limits and exclusions within your Acord liability insurance policy is crucial for effective risk management. These aspects directly impact the extent of financial protection your business receives in the event of a covered liability claim. Failing to carefully consider these factors can leave your business vulnerable to significant financial losses.
Coverage Limits and Their Implications
Coverage limits define the maximum amount your insurer will pay for covered losses under a specific policy section. These limits are usually expressed as per-occurrence limits (the maximum paid for a single incident) and aggregate limits (the maximum paid over the entire policy period). Different coverage limits significantly affect your financial exposure. A lower limit means you bear more of the cost if a claim exceeds that limit. For example, a $1 million per-occurrence limit provides less protection than a $5 million limit. Choosing appropriate limits depends on the potential severity of claims your business might face. A business with high-value assets or operations involving significant potential liabilities should opt for higher limits. Conversely, a smaller business with limited exposure may find lower limits sufficient.
Common Exclusions in Acord Liability Insurance Contracts
Several common exclusions limit the scope of coverage in Acord liability policies. These are typically listed in the policy’s exclusions section. Understanding these exclusions is vital to prevent surprises when filing a claim. Common exclusions include: intentional acts, pollution, employee injury covered by workers’ compensation, contractual liability assumed by the insured, and damage to property owned or occupied by the insured. The specific exclusions will vary based on the policy and the insured’s specific business activities.
Determining Appropriate Coverage Limits
Determining the appropriate coverage limits requires a careful assessment of your business’s risk profile. This involves identifying potential liabilities, considering the potential severity of claims, and analyzing your financial capacity to absorb losses. Factors to consider include the nature of your business, the value of your assets, your revenue, the number of employees, and the potential for lawsuits. Consulting with an insurance professional can help determine the appropriate coverage limits based on your specific circumstances. A thorough risk assessment, often conducted by an insurance broker or risk management consultant, can provide valuable insight into potential exposures and guide the selection of adequate coverage limits.
Hypothetical Scenario Illustrating the Impact of an Exclusion
Imagine a landscaping company with a general liability policy containing an exclusion for damage caused by pollution. During a project, the company accidentally spills fertilizer into a nearby stream, causing significant environmental damage and resulting in a lawsuit. The lawsuit demands $2 million in damages. If the policy’s coverage limit is $1 million, but the pollution exclusion applies, the landscaping company would be responsible for the entire $2 million in damages, even though they have liability insurance. This highlights the importance of understanding policy exclusions and the potential for significant financial liability if a claim falls under an excluded circumstance.
The Role of Insurers and Brokers
Understanding the roles of insurers and brokers is crucial for navigating the complexities of ACORD liability insurance. Both parties play distinct but interconnected roles in the process of securing and managing this type of coverage. Their responsibilities extend from initial policy application to claim settlement.
Insurance companies are the ultimate providers of coverage, bearing the financial responsibility for paying out claims filed under ACORD liability policies. Brokers, on the other hand, act as intermediaries, assisting businesses in finding suitable insurance policies and managing their insurance needs. The relationship between these two entities is symbiotic, with each relying on the other to ensure a smooth and efficient insurance process.
Insurer Responsibilities in Processing ACORD Liability Claims
Insurance companies have a defined set of responsibilities when it comes to processing ACORD liability claims. These responsibilities include promptly acknowledging the claim, conducting a thorough investigation, determining coverage, and ultimately, paying out valid claims according to the policy terms. Failure to meet these obligations can lead to legal repercussions and reputational damage for the insurer. The claims process often involves detailed documentation, communication with the policyholder and potentially third parties, and potentially engaging legal counsel if the claim is contested. A robust claims management system is essential for insurers to handle the volume and complexity of claims efficiently and fairly.
Broker Functions in Assisting Businesses with ACORD Liability Insurance
Insurance brokers act as advocates for their clients, navigating the complexities of the insurance market to find the most suitable and cost-effective ACORD liability insurance. Their functions include analyzing a business’s risk profile, identifying appropriate coverage options from multiple insurers, negotiating favorable policy terms, and assisting with the application process. Brokers also provide ongoing support, assisting with policy renewals, claim submissions, and general insurance-related queries. Their expertise can be invaluable in helping businesses understand the intricacies of their policies and ensuring they have the right level of protection.
Comparison of Services Offered by Different Types of Insurance Providers
Different insurance providers offer varying levels of service and specialization. Large national insurers may offer standardized policies and streamlined processes, but might lack the personalized attention of smaller, regional firms. Specialized insurance providers, such as those focusing on specific industries (e.g., construction, healthcare), can offer tailored policies and a deeper understanding of industry-specific risks. Direct writers, who sell policies directly to consumers without brokers, often offer competitive pricing but may limit client support and policy customization. The choice of provider depends on the specific needs and priorities of the business.
Step-by-Step Process of Obtaining ACORD Liability Insurance Through a Broker
Obtaining ACORD liability insurance through a broker typically involves a series of steps.
- Initial Consultation: The business contacts a broker to discuss its insurance needs and risk profile.
- Needs Assessment: The broker analyzes the business’s operations, identifying potential liabilities and coverage requirements.
- Policy Recommendation: Based on the assessment, the broker recommends suitable ACORD liability insurance policies from various insurers.
- Application Completion: The broker assists the business in completing the necessary application forms, including ACORD forms.
- Policy Issuance: Once the application is approved, the insurer issues the policy.
- Ongoing Management: The broker provides ongoing support, including policy reviews, renewal assistance, and claim management.
Managing and Mitigating Risks
Effective risk management is crucial for businesses seeking to minimize liability and control insurance costs. Understanding the common risks covered by ACORD liability insurance and implementing proactive mitigation strategies are key to achieving this goal. This section details common risks, mitigation techniques, and the impact of risk assessment on insurance needs and premiums.
Common Risks Covered by ACORD Liability Insurance
ACORD liability insurance policies typically cover a range of risks, depending on the specific policy and endorsements. These commonly include bodily injury and property damage caused by the insured’s negligence, advertising injury (such as libel or slander), and personal injury (such as wrongful eviction or invasion of privacy). The specific risks covered will be clearly Artikeld in the policy’s declarations and insuring agreements. Understanding these covered perils allows for targeted risk mitigation efforts.
Strategies for Mitigating Risks and Reducing Potential Claims
Mitigating risks involves proactively implementing measures to reduce the likelihood and severity of incidents leading to liability claims. For example, regular safety inspections and employee training can significantly reduce the risk of workplace accidents resulting in bodily injury claims. Similarly, implementing robust data security protocols can help mitigate the risk of data breaches leading to advertising injury claims. Furthermore, having clear and well-defined policies and procedures for all business operations helps minimize the potential for claims related to negligence or breach of contract. A comprehensive risk management plan, tailored to the specific business operations, is essential.
The Importance of Risk Assessment in Determining Insurance Needs
A thorough risk assessment is fundamental in determining the appropriate level and type of ACORD liability insurance coverage. This assessment involves identifying potential hazards, evaluating the likelihood and potential severity of losses, and analyzing the financial impact of such losses. A comprehensive risk assessment allows businesses to accurately assess their exposure to liability and secure adequate insurance coverage to protect against significant financial losses. For instance, a high-risk business, such as a construction company, will require significantly more liability coverage than a low-risk business, such as a small retail shop. The risk assessment directly informs the selection of appropriate policy limits and endorsements.
Impact of Proper Risk Management on Insurance Premiums
Effective risk management demonstrably influences insurance premiums. Insurers reward businesses that actively manage their risks by offering lower premiums. This is because proactive risk mitigation reduces the likelihood of claims, thereby lowering the insurer’s potential payout. Implementing safety programs, conducting regular risk assessments, and maintaining detailed records of risk management activities provide evidence of a commitment to risk control. This demonstrable commitment often translates into significant savings on insurance premiums, making risk management a financially sound business practice. For example, a company with a robust safety program resulting in a low incident rate can expect lower workers’ compensation premiums compared to a company with a high incident rate and limited safety measures.
Claims Process and Procedures
Filing a claim under an ACORD liability insurance policy involves a series of steps designed to ensure a fair and efficient resolution. Understanding this process is crucial for policyholders to receive the coverage they are entitled to. Prompt and accurate reporting is key to a smoother claims experience.
Steps Involved in Filing a Claim
The claims process begins immediately following an incident that may trigger liability under the policy. Policyholders should promptly notify their insurer, providing as much detail as possible. Failure to do so could jeopardize coverage. The subsequent steps often involve investigation, negotiation, and potentially, litigation.
- Initial Notification: Report the incident to your insurer as soon as possible, ideally within the timeframe specified in your policy. Provide preliminary details, including date, time, location, and a brief description of the event.
- Claim Investigation: The insurer will investigate the claim to determine liability and damages. This may involve interviewing witnesses, reviewing police reports, and assessing the extent of injuries or property damage.
- Documentation Submission: Provide the insurer with all relevant documentation, as detailed in the next section. Cooperation during this phase is vital.
- Negotiation and Settlement: The insurer will negotiate a settlement with the claimant. This may involve direct negotiations or mediation.
- Payment of Settlement: Once a settlement is reached, the insurer will pay the agreed-upon amount to the claimant, subject to policy limits and exclusions.
Required Documentation
Supporting a liability insurance claim requires comprehensive documentation to substantiate the claim’s validity and the extent of damages. The lack of crucial documentation can significantly delay or even jeopardize the claim’s success.
- Police Report: If the incident involved law enforcement, a copy of the police report is essential.
- Medical Records: In cases involving bodily injury, complete medical records, including doctor’s notes, treatment plans, and bills, are necessary to demonstrate the extent of injuries and related expenses.
- Repair Bills and Estimates: For property damage claims, detailed repair bills and estimates from qualified professionals are required.
- Witness Statements: Statements from any witnesses to the incident can provide valuable corroborating evidence.
- Photographs and Videos: Visual evidence, such as photographs and videos of the accident scene and damages, can significantly strengthen a claim.
- Policy Documentation: A copy of the insurance policy itself is crucial to confirm coverage and limits.
Best Practices for Communicating with Insurers
Effective communication is crucial for a smooth claims process. Maintaining open and honest communication with your insurer can prevent misunderstandings and delays.
- Prompt and Accurate Reporting: Report the incident promptly and provide accurate details.
- Maintain Detailed Records: Keep records of all communication with the insurer, including dates, times, and summaries of conversations.
- Respond Promptly to Requests: Respond promptly to any requests for information or documentation from the insurer.
- Be Honest and Transparent: Provide accurate and truthful information to the insurer.
- Follow Up: Follow up on the status of your claim regularly to ensure progress.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Navigating the legal and regulatory landscape surrounding ACORD liability insurance is crucial for both insurers and policyholders. Understanding the relevant laws and regulations ensures compliance, minimizes disputes, and protects all parties involved. Failure to comply can lead to significant financial and legal repercussions.
ACORD liability insurance policies, like all insurance contracts, are governed by a complex interplay of state and federal laws, as well as specific regulations pertaining to the insurance industry. These legal frameworks dictate the terms and conditions of the policy, the obligations of the insurer and the insured, and the procedures for handling claims. Moreover, the specific ACORD forms used in the policy application and administration process must adhere to strict regulatory guidelines to ensure transparency and prevent misrepresentation.
Relevant Legal Aspects of ACORD Liability Insurance Policies
Contract law forms the foundation of ACORD liability insurance policies. The policy is a legally binding agreement between the insurer and the insured, outlining the terms of coverage, exclusions, and the responsibilities of each party. Principles of contract interpretation, including the rules of construction and the doctrine of reasonable expectations, are applied in case of disputes. State laws often dictate specific requirements for policy language, such as the inclusion of mandatory provisions or prohibitions on certain types of exclusions. Furthermore, principles of good faith and fair dealing govern the relationship between the insurer and the insured throughout the policy lifecycle. Breach of contract claims are common in cases where an insurer fails to fulfill its obligations under the policy or where an insured makes a fraudulent claim.
Key Regulatory Requirements Related to ACORD Forms and Liability Coverage
State insurance departments regulate the use of ACORD forms and the content of liability insurance policies. These regulations ensure standardized reporting, facilitate efficient claims processing, and protect consumers from unfair or deceptive practices. Regulations often specify the required information to be included in ACORD forms, such as policy details, coverage limits, and exclusions. Failure to use compliant ACORD forms or to accurately complete the required fields can result in regulatory penalties for insurers and brokers. Moreover, regulations may address specific aspects of liability coverage, such as minimum coverage requirements for certain types of businesses or activities, and the inclusion of specific endorsements or riders to address particular risks.
Implications of Non-Compliance with Legal and Regulatory Standards
Non-compliance with legal and regulatory standards related to ACORD liability insurance can result in severe consequences. Insurers may face fines, license suspensions, or even revocation of their operating license. Brokers can also face disciplinary actions, including fines and the loss of their licenses. Policyholders may find their claims denied or delayed due to non-compliance with policy terms or inaccurate information provided on ACORD forms. In extreme cases, non-compliance can lead to criminal charges. For example, an insurer knowingly using non-compliant ACORD forms to underreport premiums or misrepresent coverage could face criminal prosecution for fraud.
Examples of Potential Legal Disputes Arising from ACORD Liability Insurance Claims
Several scenarios can lead to legal disputes. A common dispute arises when an insurer denies a claim based on policy exclusions or the insured’s alleged failure to meet policy conditions. For instance, a business might claim coverage for a liability claim, but the insurer denies the claim due to an exclusion for specific types of activities or failure to provide timely notice of the incident. Another potential dispute arises from disagreements over the amount of damages covered under the policy, particularly when the claim involves significant losses. Disputes can also arise from allegations of bad faith on the part of the insurer, such as unreasonable delays in processing claims or unfair settlement practices. Finally, disputes can stem from ambiguities or inconsistencies in the policy language or the ACORD forms used, requiring court interpretation to determine the parties’ rights and obligations. A classic example involves a policy with vague language regarding the definition of “accident” leading to differing interpretations by the insurer and insured.
Ending Remarks
Securing adequate ACORD liability insurance is paramount for any business operating in today’s environment. By understanding the intricacies of ACORD forms, coverage limits, exclusions, and the claims process, businesses can effectively mitigate risks and protect their financial stability. This guide has provided a framework for navigating this critical aspect of business operations, empowering you to make informed decisions and secure the appropriate level of liability protection. Remember to consult with a qualified insurance professional to tailor your policy to your specific needs and circumstances.
FAQ Summary
What is the difference between ACORD and other liability insurance?
ACORD forms are standardized documents used in the insurance industry to streamline information exchange. While ACORD liability insurance itself isn’t a distinct type of coverage, it utilizes these standardized forms to document and manage liability policies. Other liability insurance types may use different forms or processes.
How often should I review my ACORD liability insurance policy?
It’s recommended to review your policy annually, or whenever there are significant changes to your business operations, such as expansion, new products/services, or changes in risk profile. This ensures your coverage remains adequate.
What happens if I fail to disclose relevant information on an ACORD form?
Non-disclosure of material information on an ACORD form can lead to policy denial or reduced coverage in the event of a claim. Accuracy and completeness are crucial.
Can I obtain ACORD liability insurance online?
While some online platforms offer insurance quotes, obtaining ACORD liability insurance often involves working directly with an insurance broker or agent who can assist with the application and policy selection process.