Navigating the world of insurance can feel like deciphering a complex code, especially when the goal is finding affordable insurance rates. The cost of health, life, auto, or home insurance significantly impacts personal finances, leaving many feeling overwhelmed and unsure where to begin. This guide demystifies the process, providing practical strategies and insights to help you secure the best coverage without breaking the bank. We’ll explore the factors influencing premiums, uncover resources for finding affordable options, and offer long-term strategies for maintaining financial health and insurance affordability.
Understanding what constitutes “affordable” is crucial and varies greatly depending on individual circumstances. This guide examines the key factors impacting insurance costs, including age, health, location, and coverage choices. We’ll delve into government assistance programs, compare different insurance providers, and equip you with the knowledge to confidently navigate the insurance application process and make informed decisions about your coverage.
Defining “Affordable Insurance Rates”
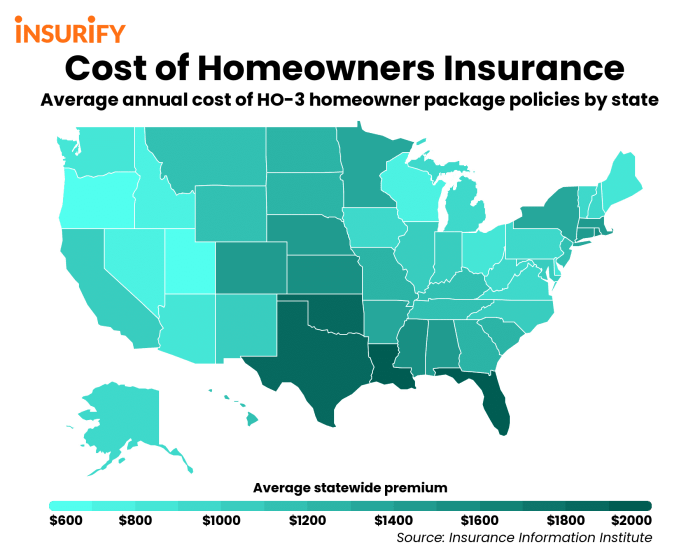
Determining what constitutes “affordable” insurance rates is complex and highly subjective. It’s not simply a fixed dollar amount; rather, it’s a relative measure deeply intertwined with an individual’s financial situation, geographic location, and specific insurance needs. A rate considered affordable for a high-income earner in a low-cost-of-living area might be prohibitively expensive for someone with a lower income in a high-cost area.
Affordability is primarily judged by comparing the cost of insurance premiums to an individual’s disposable income. A generally accepted guideline is that insurance premiums shouldn’t exceed a certain percentage of one’s income (often cited as 10-15%, though this can vary). However, this percentage can be influenced by many factors. For example, someone with pre-existing health conditions might need more comprehensive coverage, increasing the percentage of their income allocated to insurance. Conversely, a younger, healthier individual might find a lower-cost plan perfectly adequate. Geographic location plays a crucial role, with premiums varying significantly across states and even within the same state due to factors like healthcare provider costs and the prevalence of specific health issues.
Insurance Cost Ranges and Influencing Factors
The cost of insurance varies significantly depending on the type of coverage. Below is a table illustrating average monthly cost ranges for several common insurance types. Remember, these are averages and actual costs can vary substantially.
| Insurance Type | Average Monthly Cost (Low) | Average Monthly Cost (High) | Factors Influencing Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Health Insurance (Individual Plan) | $200 | $1000+ | Age, health status, location, plan type (e.g., Bronze, Gold), deductible, copay |
| Auto Insurance | $50 | $200+ | Driving record, vehicle type, location, coverage level (liability, collision, comprehensive) |
| Homeowners Insurance | $50 | $200+ | Home value, location, coverage level, safety features |
| Renters Insurance | $15 | $50 | Coverage level, location, value of belongings |
Subjectivity of Affordability Across Demographics
Affordability is inherently subjective and varies significantly across different demographics. A family with multiple children and a single income may struggle to afford insurance premiums that a dual-income household with no children finds manageable. Similarly, seniors on fixed incomes may face challenges affording premiums compared to younger adults with higher earning potential. Individuals with pre-existing conditions often require more extensive coverage, leading to higher premiums and potentially impacting their perception of affordability. Ultimately, determining whether insurance rates are “affordable” requires a personalized assessment considering individual financial circumstances and needs.
Factors Influencing Insurance Costs

Several interconnected factors determine the cost of insurance premiums. Understanding these elements empowers consumers to make informed decisions and potentially secure more affordable coverage. This section details the key influences on insurance costs, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of how premiums are calculated.
Age
Age significantly impacts insurance premiums across various types of insurance. For health insurance, older individuals generally face higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of requiring more extensive medical care. Conversely, younger, healthier individuals typically enjoy lower rates. Auto insurance premiums also often reflect age, with younger drivers (especially those with less driving experience) facing higher premiums due to statistically higher accident rates. This reflects the actuarial risk assessment inherent in insurance pricing.
Health History and Lifestyle Choices
An individual’s health history and lifestyle significantly influence their insurance premiums, particularly in health insurance. Pre-existing conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease, can lead to higher premiums, as insurers assess the increased risk of future claims. Similarly, lifestyle choices like smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, or a lack of physical activity can elevate premiums. Insurers consider these factors as indicators of potential health risks and adjust premiums accordingly. For example, a smoker might pay considerably more for health insurance than a non-smoker of the same age and gender.
Location
Geographic location plays a crucial role in determining insurance costs. Areas with higher crime rates generally result in higher premiums for home and auto insurance due to the increased risk of theft, accidents, and property damage. Similarly, areas prone to natural disasters, such as hurricanes or earthquakes, will see higher premiums for homeowners’ insurance. The cost of healthcare services also varies geographically; thus, health insurance premiums can differ significantly based on location. For instance, someone living in a major metropolitan area with high healthcare costs will typically pay more than someone in a rural area.
Coverage Type and Deductible Choices
The type of coverage selected directly impacts the cost of insurance. Comprehensive auto insurance, for example, is more expensive than liability-only coverage because it offers broader protection. Similarly, higher levels of health insurance coverage, such as platinum plans, tend to have higher premiums than lower coverage plans, such as bronze plans. Deductible choices also influence premiums. A higher deductible (the amount the insured pays out-of-pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in) typically results in lower premiums, while a lower deductible leads to higher premiums. This is because the insured assumes more of the initial risk with a higher deductible.
Strategies to Lower Insurance Premiums
Several strategies can help individuals lower their insurance premiums.
- Maintain a good driving record: Avoiding accidents and traffic violations significantly reduces auto insurance premiums.
- Improve your health: Quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and managing chronic conditions can lower health insurance premiums.
- Bundle policies: Combining multiple insurance policies (auto, home, life) with the same insurer often results in discounts.
- Shop around and compare rates: Obtaining quotes from multiple insurers ensures you find the most competitive rates.
- Increase your deductible: Opting for a higher deductible can lower your premiums, although it increases your out-of-pocket expenses in case of a claim.
- Consider discounts: Many insurers offer discounts for things like safety features in your car, security systems in your home, or completing driver’s education courses.
Finding Affordable Insurance Options
Securing affordable insurance requires a proactive approach and a thorough understanding of available resources. This section details various strategies to identify and select cost-effective insurance plans that meet your needs. We will explore effective methods for comparing providers and navigating the application process.
Finding the right insurance plan often involves comparing multiple providers and utilizing available tools. This process can seem daunting, but with a systematic approach, it becomes manageable and even rewarding.
Utilizing Online Comparison Tools
Online comparison websites offer a convenient way to quickly assess various insurance plans from different providers. These platforms typically allow users to input their personal details and desired coverage levels, generating a list of suitable plans with their respective premiums. By comparing quotes side-by-side, consumers can identify the most affordable options that align with their requirements. Many of these websites also provide customer reviews and ratings, allowing for informed decision-making. Examples of such websites include [insert examples of reputable comparison websites, mentioning their geographical limitations if any, e.g., “in the US, sites like…”]. Remember to check the accuracy and timeliness of the information displayed.
Consulting with Insurance Brokers
Insurance brokers act as intermediaries between consumers and insurance companies. Their expertise can be invaluable in navigating the complexities of insurance plans and finding suitable, affordable options. Brokers often have access to a wider range of plans than those available through online comparison tools, including potentially less advertised options from smaller providers. They can also provide personalized guidance based on individual circumstances, offering valuable insights and support throughout the process. The cost of using a broker can vary; some brokers work on commission, while others charge a fee. It’s important to clarify their fee structure upfront.
Comparing Insurance Providers
A direct comparison of different insurance providers is crucial for identifying the best value. The following table illustrates a simplified comparison; actual provider strengths and weaknesses can vary depending on location and specific policy details. Remember to always check the fine print and policy details.
| Provider | Strengths (Affordability) | Weaknesses (Affordability) |
|---|---|---|
| Provider A (Example) | Competitive premiums for basic coverage, strong online tools | Limited customer service, potentially higher premiums for comprehensive coverage |
| Provider B (Example) | Excellent customer service, wide range of plans | Premiums may be higher compared to some competitors, less user-friendly website |
| Provider C (Example) | Discounts for bundling policies, strong financial stability | Less flexible policy options, limited online tools |
Navigating the Insurance Application Process
The insurance application process can be streamlined by following a structured approach.
- Gather necessary information: This includes personal details, driving history (for auto insurance), medical history (for health insurance), and property details (for homeowners or renters insurance).
- Compare quotes: Use online comparison tools and consult with brokers to obtain multiple quotes from different providers.
- Review policy details: Carefully examine the policy documents, paying close attention to coverage limits, deductibles, and exclusions.
- Complete the application: Fill out the application accurately and completely. Inaccurate information can lead to delays or even policy rejection.
- Submit supporting documents: Provide any required supporting documentation, such as proof of address or medical records.
- Review and accept the policy: Once the application is approved, review the policy details one last time before accepting it.
- Make timely payments: Ensure prompt payment of premiums to avoid policy cancellation.
Government Subsidies and Assistance Programs
Securing affordable health insurance can be challenging, but various government subsidies and assistance programs aim to alleviate this burden. These programs offer financial aid to individuals and families who meet specific eligibility criteria, making healthcare coverage more accessible. Understanding these programs and how to access them is crucial for those seeking affordable insurance.
Government subsidies and assistance programs are designed to reduce the cost of health insurance premiums, deductibles, and co-pays. Eligibility is typically based on income, household size, and citizenship status. The specific requirements and available benefits vary depending on the program and the location. Many programs operate at the federal level, while others are administered at the state or local level. Applying for these programs often involves completing an application form and providing supporting documentation, such as proof of income and household size.
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) Subsidies
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) offers premium tax credits and cost-sharing reductions to eligible individuals and families purchasing health insurance through the Health Insurance Marketplaces (also known as exchanges). These subsidies lower the monthly premiums and out-of-pocket costs associated with health insurance plans. Eligibility is determined based on income, household size, and the cost of the second-lowest-cost silver plan available in the individual’s area. Applicants typically provide documentation such as tax returns, pay stubs, and proof of citizenship or immigration status. The application process is usually completed online through the Healthcare.gov website or a state-based marketplace. The amount of the subsidy varies depending on the individual’s income and the cost of the chosen plan. For example, a family earning $60,000 annually might receive a significant reduction in their monthly premium, making a previously unaffordable plan financially feasible.
Medicaid and CHIP
Medicaid and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) are government-sponsored health insurance programs for low-income individuals and families. Medicaid eligibility varies by state, but generally includes individuals and families below a certain income threshold. CHIP provides low-cost health coverage to children in families who earn too much to qualify for Medicaid but cannot afford private insurance. Applying for Medicaid or CHIP involves completing an application form through the state’s Medicaid agency. Required documentation typically includes proof of income, residency, and identity. The specific requirements and benefits vary from state to state. For instance, some states may offer more comprehensive coverage than others, and income limits may differ.
Medicare Savings Programs
Medicare Savings Programs help low-income seniors and people with disabilities pay their Medicare premiums, deductibles, and coinsurance. These programs are administered by state Medicaid agencies. Eligibility is based on income and resource limits. Individuals apply through their state’s Medicaid agency, providing documentation such as proof of income, assets, and Medicare enrollment. These programs can significantly reduce the out-of-pocket costs associated with Medicare, ensuring that seniors and people with disabilities can access essential healthcare services. For example, a Medicare Savings Program might cover the entire monthly Part B premium for a qualified individual.
Understanding Policy Details and Coverage
Securing affordable insurance is only half the battle; understanding your policy’s intricacies is crucial to ensure you receive the coverage you need when you need it. Failing to grasp the terms, conditions, and limitations can lead to unexpected out-of-pocket expenses and dissatisfaction. This section clarifies key aspects of policy details and their impact on your overall insurance costs.
Understanding your policy’s terms, conditions, and coverage limitations is vital for maximizing the value of your insurance and avoiding financial surprises. Many policies contain clauses that can significantly affect your out-of-pocket costs, either by limiting coverage or increasing premiums. Careful review of these aspects ensures you’re getting the most for your money.
Common Policy Clauses and Their Affordability Implications
Several common clauses within insurance policies can directly influence affordability. For example, deductibles, co-pays, and exclusions are frequently cited as examples of such clauses. Understanding their implications is essential for making informed decisions about your coverage.
Coverage Options and Cost Implications
Different coverage options offer varying levels of protection and consequently, different price points. Choosing the right coverage level involves balancing your risk tolerance with your budget. The following table illustrates some common coverage options and their cost implications:
| Coverage Type | Description | Typical Cost Impact | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deductible | The amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage begins. | Higher deductible = Lower premium; Lower deductible = Higher premium | A $1,000 deductible on a health insurance plan means you pay the first $1,000 of medical expenses before your insurance kicks in. A higher deductible, say $5,000, would result in a lower monthly premium but a higher initial cost should you need care. |
| Co-pay | A fixed amount you pay for a medical service, such as a doctor’s visit. | Higher co-pay = Lower premium; Lower co-pay = Higher premium | A $25 co-pay for a doctor’s visit means you pay $25 each time you see a doctor, regardless of the total cost of the visit. Lower co-pays mean lower out-of-pocket costs per visit but usually higher premiums. |
| Co-insurance | The percentage of costs you share with your insurer after your deductible is met. | Lower co-insurance percentage = Higher premium; Higher co-insurance percentage = Lower premium | A 20% co-insurance means you pay 20% of the medical bill after your deductible is met. A lower co-insurance percentage (e.g., 10%) means lower out-of-pocket costs but higher premiums. |
| Exclusions | Specific services or conditions not covered by your insurance policy. | Policies with fewer exclusions generally cost more. | Some policies might exclude pre-existing conditions or experimental treatments. A policy with fewer exclusions will offer broader coverage but will likely be more expensive. |
Long-Term Strategies for Affordable Insurance
Securing affordable insurance isn’t just about finding the cheapest plan this year; it’s about developing a long-term strategy that protects your financial well-being while minimizing costs over time. Proactive steps taken today can significantly impact your insurance premiums for years to come. This involves a two-pronged approach: maintaining good health and practicing sound financial planning.
Maintaining good health and strong financial habits are crucial for keeping long-term insurance costs manageable. By focusing on preventative care and responsible financial planning, you can significantly reduce your risk profile, leading to lower premiums and greater financial security. This proactive approach translates into long-term savings and peace of mind.
Preventative Healthcare and Its Impact on Insurance Costs
Preventative healthcare plays a significant role in reducing long-term insurance costs. Regular check-ups, screenings, and vaccinations can detect and address potential health issues early, preventing them from developing into more serious and costly conditions. For example, regular blood pressure checks can help prevent hypertension, a major risk factor for heart disease, while routine dental checkups can prevent costly dental procedures later in life. These proactive measures demonstrate to insurers a lower risk profile, often resulting in lower premiums. Furthermore, maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise reduces the risk of developing conditions like diabetes and heart disease, further impacting your insurance rates positively.
Financial Planning for Long-Term Insurance Expenses
Effective financial planning is essential for managing insurance costs over the long term. This involves budgeting for insurance premiums, exploring different insurance options, and considering strategies to minimize expenses. For instance, building an emergency fund can help cover unexpected medical expenses, reducing the reliance on insurance payouts and potentially lowering premiums in the long run. Regularly reviewing your insurance coverage to ensure it aligns with your current needs and risk profile is also vital. Consider factors such as life changes (marriage, children, career shifts) which can impact your insurance requirements. Proactive planning allows you to adapt your coverage and payment strategies, preventing financial strain and maintaining affordability. For example, someone who anticipates a significant career change that might lead to a loss of employer-sponsored insurance can proactively start researching individual health insurance options well in advance, allowing ample time for comparison and selection. This careful planning minimizes the risk of a lapse in coverage and avoids potential penalties.
Last Point
Securing affordable insurance rates requires proactive planning and informed decision-making. By understanding the factors influencing premiums, exploring available resources, and implementing long-term strategies, you can significantly reduce your insurance costs and protect your financial future. Remember to regularly review your policy and coverage needs to ensure you maintain adequate protection while staying within your budget. Empowering yourself with knowledge is the first step toward achieving affordable and comprehensive insurance coverage.
Questions Often Asked
What is a deductible, and how does it affect my insurance costs?
A deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Higher deductibles generally lead to lower monthly premiums, but you’ll pay more upfront if you need to file a claim.
Can I get insurance if I have pre-existing conditions?
In many countries, including the US under the Affordable Care Act, insurance companies cannot deny coverage or charge higher premiums based solely on pre-existing conditions. However, the specific rules vary by location and policy.
How often can I change my insurance plan?
The frequency with which you can change your insurance plan depends on your location and the type of insurance. Open enrollment periods exist for many plans, while others may allow changes due to life events (marriage, job loss).
What is the difference between term life insurance and whole life insurance?
Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period, typically at a lower cost. Whole life insurance offers lifelong coverage but is generally more expensive.