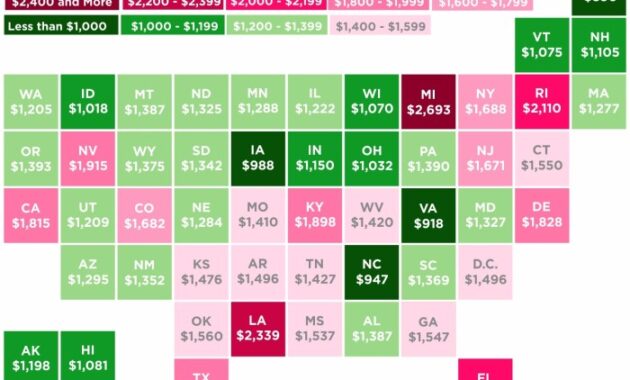
Navigating the complex landscape of auto insurance can be daunting, especially when considering the significant variations in cost across different states. This guide delves into the factors influencing auto insurance premiums, providing a state-by-state analysis to help you understand what contributes to the price you pay and how you might potentially save money. We’ll explore everything from minimum coverage requirements and state regulations to the impact of your driving record and vehicle type.
Understanding the nuances of auto insurance cost by state is crucial for making informed decisions about your coverage. Whether you’re a new driver, a seasoned motorist, or simply looking to optimize your insurance budget, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of this essential aspect of car ownership.
Factors Affecting Auto Insurance Premiums
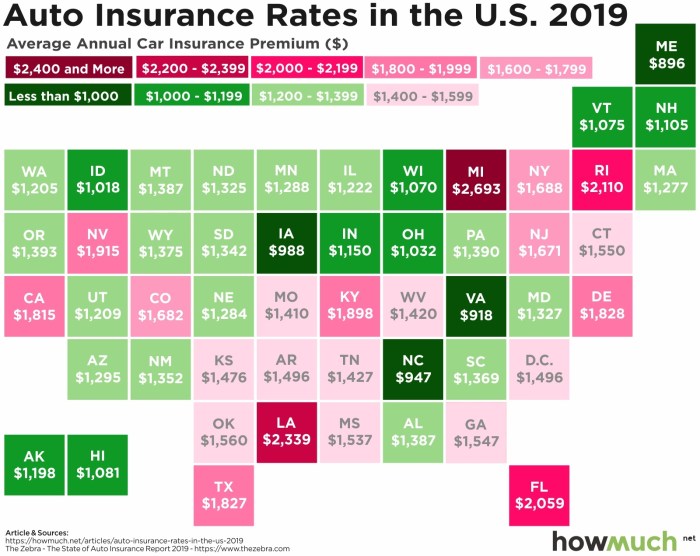
Auto insurance premiums are not a one-size-fits-all cost. Several interconnected factors influence the final price you pay, impacting the overall affordability and accessibility of this essential coverage. Understanding these factors can empower you to make informed decisions and potentially lower your premiums.
Several key elements contribute significantly to the calculation of your auto insurance premium. These factors are often analyzed in combination to create a comprehensive risk assessment.
Driver Demographics
Insurers carefully consider driver characteristics to assess risk. Younger and older drivers often face different premium structures than those in the mid-range age group. Gender also plays a role, though its impact varies by location and insurer. Driving history, encompassing accidents, tickets, and claims, is a paramount factor influencing premium costs.
- Age: Younger drivers (typically under 25) generally pay higher premiums due to statistically higher accident rates. Older drivers (over 65) might also see increased premiums, sometimes due to age-related driving challenges. Drivers in the 25-65 age range typically fall into the lowest risk category.
- Gender: Historically, men have been statistically associated with higher accident rates than women, leading to potentially higher premiums for male drivers in some regions. However, this gap is narrowing in many areas.
- Driving History: A clean driving record with no accidents or traffic violations translates to lower premiums. Conversely, multiple accidents or serious traffic offenses will significantly increase your insurance costs. The severity and frequency of incidents directly impact the assessment of risk.
Vehicle Characteristics
The type of vehicle you drive is another crucial factor in determining your insurance premium. Insurers consider various aspects of your car to evaluate its potential for damage and the associated repair costs.
- Make and Model: Some car makes and models are statistically more prone to accidents or theft, resulting in higher premiums. Luxury vehicles, often associated with higher repair costs, also typically carry higher insurance rates.
- Year: Newer cars generally have more advanced safety features and are often worth more, leading to higher premiums due to higher repair costs. Older vehicles, while potentially cheaper to insure, may lack safety features and be more prone to mechanical issues.
- Safety Features: Cars equipped with anti-lock brakes (ABS), airbags, electronic stability control (ESC), and other advanced safety technologies often qualify for discounts because they reduce the likelihood and severity of accidents.
Geographic Location
Where you live significantly impacts your auto insurance rates. Insurers analyze accident rates, crime statistics, and the overall risk profile of different areas to determine premiums.
- Urban vs. Rural: Urban areas generally have higher accident rates and higher vehicle theft rates compared to rural areas, leading to higher insurance premiums in cities and densely populated suburbs.
- Accident Rates: Areas with high accident rates, regardless of urban or rural classification, typically have higher insurance premiums due to the increased risk of claims.
Coverage Levels
The type and amount of coverage you choose directly affect your premium. Higher coverage limits generally mean higher premiums, but also greater financial protection in the event of an accident.
- Liability Coverage: This covers damages to other people and their property if you cause an accident. Higher liability limits provide more extensive protection but increase your premium.
- Collision Coverage: This covers damage to your vehicle in an accident, regardless of fault. This coverage is optional but crucial for protecting your financial investment in your car.
- Comprehensive Coverage: This covers damage to your vehicle from events other than collisions, such as theft, vandalism, or natural disasters. This coverage is also optional, but valuable for mitigating losses from non-accident related incidents.
State-Specific Regulations and Laws
State regulations significantly impact auto insurance costs. Variations in minimum coverage requirements, the presence or absence of no-fault laws, and other legislative initiatives create a diverse landscape of insurance pricing across the United States. Understanding these differences is crucial for consumers seeking the best value for their insurance needs.
State laws directly influence the amount drivers pay for auto insurance. These laws set minimum coverage requirements, dictate how accident claims are handled, and shape the overall cost of insurance for individuals and companies. The following sections explore these key aspects of state-specific regulations and their impact on auto insurance premiums.
Minimum Insurance Coverage Requirements by State
The minimum amount of insurance coverage required varies considerably from state to state. These minimums typically cover bodily injury liability, property damage liability, and sometimes uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage. Failure to carry at least the minimum required coverage can result in significant penalties.
| State | Minimum Coverage Requirements (Example – May vary; check your state’s DMV for accurate information) |
|---|---|
| California | $15,000 bodily injury liability per person, $30,000 bodily injury liability per accident, $5,000 property damage liability |
| Texas | $30,000 bodily injury liability per person, $60,000 bodily injury liability per accident, $25,000 property damage liability |
| New York | $25,000 bodily injury liability per person, $50,000 bodily injury liability per accident, $10,000 property damage liability |
| Florida | $10,000 bodily injury liability per person, $20,000 bodily injury liability per accident, $10,000 property damage liability |
Examples of State-Specific Laws Impacting Auto Insurance Costs
Several state-level laws and initiatives directly affect auto insurance premiums. No-fault laws, for instance, dictate how accident claims are handled, potentially influencing the frequency and severity of claims. Tort reform legislation often limits the amount of damages that can be awarded in lawsuits, impacting insurance payouts and, consequently, premiums.
For example, states with no-fault systems tend to have lower premiums because injured parties are primarily compensated by their own insurance, reducing litigation and associated costs. Conversely, states with more permissive tort laws might have higher premiums due to the potential for larger payouts in lawsuits. Similarly, states with stricter regulations on insurance companies’ rate increases can keep premiums lower.
Comparison of Regulatory Environments in Three States
Let’s compare California, Texas, and Florida. California has relatively high minimum coverage requirements and a complex regulatory environment, leading to moderately high insurance costs. Texas has lower minimum coverage requirements and a more deregulated market, resulting in some of the lowest average insurance premiums in the nation. Florida, on the other hand, has relatively low minimum coverage requirements but a high frequency of accidents and lawsuits, leading to high average insurance premiums despite the lower minimums. These examples illustrate how a combination of factors—minimum coverage, tort laws, and the frequency of accidents—contributes to the overall cost of auto insurance in a given state.
Cost Comparison and Savings Strategies
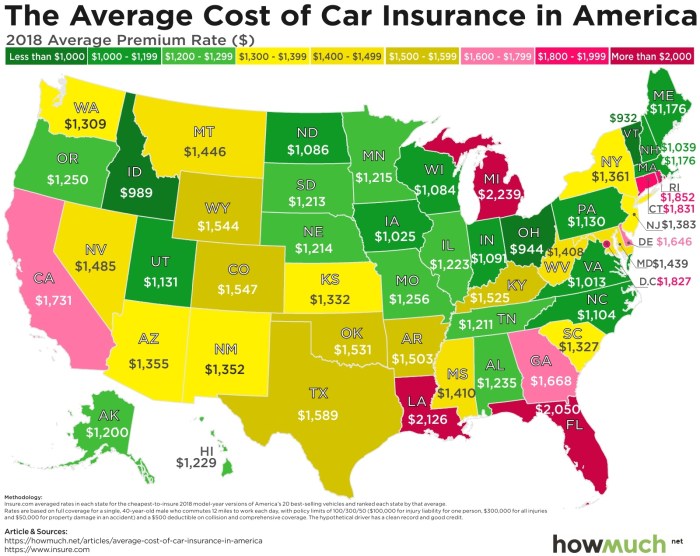
Understanding the variations in auto insurance costs across different providers is crucial for securing the best value for your money. This section will explore how to compare costs and implement strategies to potentially reduce your premiums. We’ll examine specific examples and illustrate the potential savings available.
Comparative Analysis of Auto Insurance Costs
The following table illustrates potential cost differences for a hypothetical 30-year-old driver with a clean driving record in California, driving a 2020 Honda Civic, for liability-only coverage. These are illustrative examples and actual costs will vary based on individual circumstances and the specific policy details offered by each insurer. Remember to obtain personalized quotes from multiple companies for accurate comparison.
| Insurance Company | Annual Premium (Estimate) |
|---|---|
| Company A | $800 |
| Company B | $950 |
| Company C | $750 |
| Company D | $1050 |
Strategies for Lowering Auto Insurance Premiums
Several actions can significantly influence your auto insurance premium. Proactive measures often lead to substantial savings over time.
Implementing these strategies can result in considerable cost reductions. For instance, maintaining a clean driving record can lead to significant discounts, while bundling policies can offer substantial savings compared to purchasing separate policies for car and home insurance.
- Maintain a clean driving record: Avoid accidents and traffic violations. Many insurers offer significant discounts for drivers with no accidents or tickets for several years.
- Complete a defensive driving course: Successfully completing a state-approved defensive driving course often results in premium reductions, demonstrating your commitment to safe driving practices.
- Bundle your insurance policies: Combining your auto insurance with other types of insurance, such as homeowners or renters insurance, frequently leads to discounts from insurers.
- Increase your deductible: Choosing a higher deductible (the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in) will generally lower your premium. However, weigh this against your ability to cover a higher deductible in the event of a claim.
- Choose a car with safety features: Vehicles equipped with anti-theft devices, airbags, and other safety features are often associated with lower insurance premiums.
- Pay your premiums on time: Consistent and timely payments can demonstrate financial responsibility and potentially lead to discounts or better rates.
- Shop around and compare quotes: Regularly comparing quotes from different insurance providers ensures you’re getting the best possible rate. Market conditions and insurer offerings change frequently.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Usage-Based Insurance
Usage-based insurance (UBI), also known as pay-as-you-drive insurance, is a type of auto insurance that bases your premium on your actual driving habits. Data is collected through a device plugged into your car’s diagnostic port or through a smartphone app.
While UBI offers the potential for significant savings for safe drivers, it’s crucial to understand its limitations. For example, drivers who frequently travel long distances or engage in higher-risk driving behaviors may not see substantial benefits.
- Benefits: Lower premiums for safe drivers, accurate reflection of driving habits, potential for significant savings for low-mileage drivers.
- Drawbacks: Privacy concerns regarding data collection, potential for higher premiums for drivers with less-than-ideal driving habits, reliance on technology and potential for technical issues.
Illustrative Examples
To better understand how various factors influence auto insurance costs, let’s examine two hypothetical scenarios and a visual representation of income correlation with insurance premiums across different states. These examples illustrate the complexity of auto insurance pricing.
Consider two drivers: Sarah, a 28-year-old with a clean driving record, and David, a 25-year-old with one speeding ticket. Sarah drives a fuel-efficient sedan, while David drives a high-performance sports car. Sarah lives in rural Iowa, while David lives in urban Miami, Florida.
Scenario Comparison: Sarah and David
Sarah’s clean driving record, coupled with her choice of vehicle and location, will likely result in a significantly lower premium compared to David. Iowa, generally, has lower insurance rates than Florida due to factors such as lower accident rates and less severe weather conditions. David’s speeding ticket, high-performance vehicle, and location in a high-risk urban area will contribute to higher premiums. The difference in their premiums could be substantial, even if both have similar coverage levels.
For instance, Sarah might pay around $800 annually for comprehensive coverage, while David’s premium could easily exceed $2000, reflecting the increased risk associated with his profile. This difference highlights the significant impact of individual factors on insurance costs.
Correlation Between Average Income and Auto Insurance Cost
A hypothetical scatter plot could visually represent the correlation between average state income and average auto insurance costs. The horizontal axis (x-axis) would represent average state income (in thousands of dollars), while the vertical axis (y-axis) would represent average annual auto insurance cost (in dollars).
The graph would likely show a positive, but not necessarily perfectly linear, correlation. States with higher average incomes might tend to have higher average auto insurance costs, though this relationship isn’t always straightforward. This is because higher income areas often have more expensive vehicles, higher population density leading to more accidents, and potentially higher repair costs. However, outliers could exist – a state with a high average income but relatively low accident rates might fall below the general trend line. The graph might also show distinct clusters of states, grouping states with similar economic characteristics and insurance regulatory environments.
For example, states like California and New York, known for higher costs of living and higher average incomes, might be clustered at the higher end of both axes, while states like Nebraska and Oklahoma might be clustered towards the lower end, representing lower income and lower average insurance costs. The overall trend would illustrate a general relationship, highlighting how economic factors indirectly influence auto insurance pricing across different states.
Outcome Summary
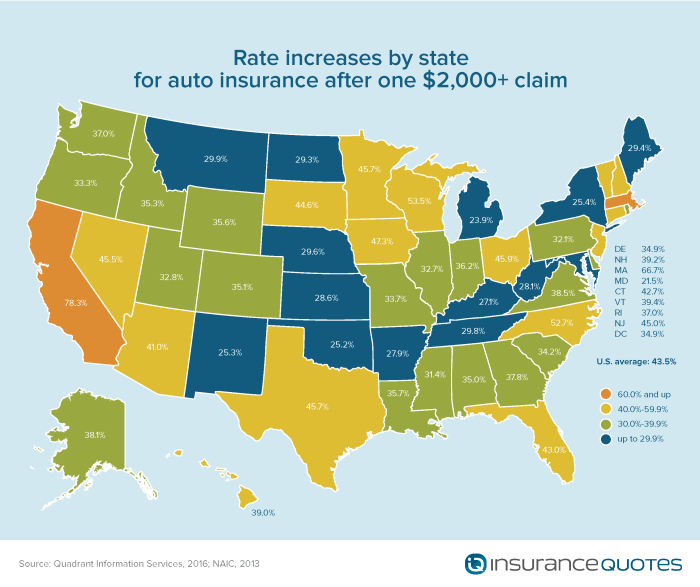
Ultimately, the cost of auto insurance is a multifaceted issue shaped by a complex interplay of individual circumstances, state regulations, and market dynamics. By understanding the factors influencing premiums and employing strategic cost-saving measures, drivers can effectively manage their insurance expenses and secure the appropriate level of coverage. This guide serves as a valuable resource for navigating the intricacies of auto insurance, empowering you to make informed choices and achieve financial peace of mind.
Questions Often Asked
What is the average cost of full coverage auto insurance?
The average cost of full coverage auto insurance varies significantly by state and individual circumstances. It can range from a few hundred dollars annually to well over $2000, depending on factors like age, driving history, and the vehicle itself.
Can I get car insurance without a driver’s license?
Generally, no. Most insurance companies require a valid driver’s license to insure a vehicle. Exceptions might exist for specific situations, but it’s rare.
How often are auto insurance rates reviewed?
Auto insurance rates are typically reviewed and adjusted annually, or sometimes even more frequently, depending on the insurer and changes in your driving record or risk profile.
What is SR-22 insurance?
SR-22 insurance is a certificate of insurance that proves you maintain the minimum liability coverage required by your state. It’s often required after a serious driving offense.