
Securing the right car insurance policy is a crucial step in responsible vehicle ownership. Understanding the diverse options available, the factors influencing premiums, and the intricacies of claims processes can feel overwhelming. This guide aims to demystify car insurance, providing a comprehensive overview of policy types, cost considerations, and crucial procedural steps, empowering you to make informed decisions that best protect your financial interests and peace of mind.
From liability coverage to comprehensive protection, the world of car insurance offers a range of choices tailored to individual needs and risk profiles. This exploration will delve into the specifics of each policy type, highlighting key differences and benefits. We will also examine how factors such as driving history, vehicle type, and location significantly impact premiums, along with strategies to potentially reduce costs. Finally, we’ll navigate the process of filing a claim, understanding policy documents, and making informed choices about coverage levels.
Types of Car Insurance Policies
Choosing the right car insurance policy can seem daunting, but understanding the different types available empowers you to make an informed decision that best protects you and your vehicle. This section details the common types of car insurance coverage, highlighting their key features and benefits. Remember that specific coverage details and costs vary by insurer and location.
Car insurance policies are designed to cover various risks associated with car ownership. Understanding these different types of coverage is crucial for selecting a policy that adequately addresses your individual needs and financial situation.
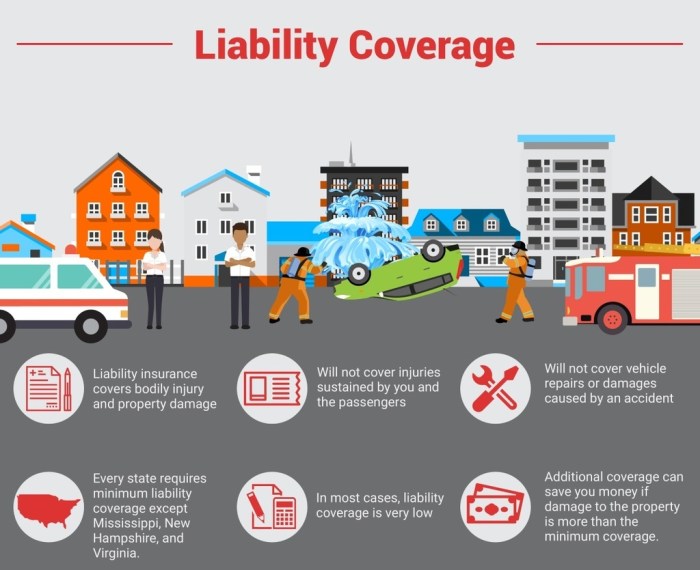
Liability Coverage
Liability insurance covers damages or injuries you cause to others in an accident. It’s usually divided into bodily injury liability and property damage liability. Bodily injury liability covers medical expenses and other damages for injuries to others. Property damage liability covers repairs or replacement costs for the other person’s vehicle or property. Most states require a minimum amount of liability coverage. For example, a policy might have limits of $25,000 per person and $50,000 per accident for bodily injury and $25,000 for property damage. This means the insurance company would pay a maximum of $25,000 for injuries to one person, up to $50,000 for injuries to multiple people in a single accident, and up to $25,000 for property damage.
Collision Coverage
Collision coverage pays for repairs or replacement of your vehicle if it’s damaged in an accident, regardless of fault. This means even if you cause the accident, your insurance will cover the damage to your car. The amount paid will usually be the actual cash value of your vehicle minus your deductible. For example, if your car is worth $10,000, and your deductible is $500, the insurance company would pay up to $9,500 for repairs or replacement. Collision coverage is optional but highly recommended.
Comprehensive Coverage
Comprehensive coverage protects your vehicle from damage caused by events other than collisions, such as theft, vandalism, fire, hail, or natural disasters. Like collision coverage, the amount paid is usually the actual cash value minus your deductible. This provides broader protection than collision coverage alone. For instance, if a tree falls on your car during a storm, comprehensive coverage would help pay for the repairs.
Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage
Uninsured/underinsured motorist (UM/UIM) coverage protects you if you’re involved in an accident with a driver who doesn’t have insurance or doesn’t have enough insurance to cover your damages. This is crucial because it can cover your medical bills, lost wages, and vehicle repairs even if the other driver is at fault and lacks sufficient insurance. UM coverage covers injuries caused by an uninsured driver, while UIM coverage steps in when the other driver’s liability limits are insufficient to cover your losses.
| Policy Type | Coverage | What it Covers | Optional? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liability | Bodily Injury & Property Damage | Damages and injuries you cause to others | No (minimum limits required in most states) |
| Collision | Damage to Your Vehicle | Repairs or replacement of your vehicle after an accident, regardless of fault | Yes |
| Comprehensive | Damage to Your Vehicle (Non-Collision) | Damage from events like theft, vandalism, fire, or weather | Yes |
| Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist | Injuries Caused by Un/Underinsured Drivers | Covers your losses if the other driver is uninsured or underinsured | Yes |
Understanding Policy Documents

Your car insurance policy is a legally binding contract. Understanding its contents is crucial for ensuring you receive the coverage you expect and avoid any unexpected costs or disputes. This section will guide you through the key components of a typical policy document.
A thorough review of your policy document is essential to avoid misunderstandings and ensure you’re adequately protected. Familiarizing yourself with the terms and conditions will help you make informed decisions and prevent potential problems down the line. Failing to understand your policy could lead to disputes with your insurer during a claim.
Common Policy Document Sections
Most car insurance policies share a similar structure, though the specific wording and details may vary between insurers. Familiarizing yourself with these common sections will make navigating your policy significantly easier.
- Declaration Page: This is the summary page. It provides key information such as your name, address, vehicle details, policy number, coverage start and end dates, and the premium amount.
- Insuring Agreement: This section Artikels the insurer’s promise to provide coverage under specific circumstances. It details the types of coverage you’ve purchased (e.g., liability, collision, comprehensive).
- Definitions: This section clarifies the meaning of key terms used throughout the policy. Understanding these definitions is critical for interpreting the policy’s provisions correctly.
- Exclusions: This crucial section lists situations or events that are not covered by your insurance policy. Carefully reviewing this section will help you understand the limitations of your coverage.
- Conditions: This section details the responsibilities of both the insured (you) and the insurer. It Artikels your duties in the event of an accident, such as reporting the incident promptly.
- Premium and Payment Information: This section details your payment schedule, methods of payment, and any applicable discounts or surcharges.
Interpreting Key Information
Effectively interpreting your policy requires careful attention to detail. Focusing on specific aspects will help you understand your rights and responsibilities.
- Coverage Limits: These specify the maximum amount the insurer will pay for a particular type of claim (e.g., $100,000 for bodily injury liability). Understanding these limits is vital to avoid financial exposure in the event of an accident.
- Deductibles: This is the amount you must pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Higher deductibles usually result in lower premiums, and vice versa.
- Premium Calculation: Your premium is determined by various factors, including your driving record, age, location, vehicle type, and the coverage you select. Understanding these factors helps you assess the value of your policy.
The Importance of Policy Review
Regularly reviewing your car insurance policy is a proactive step to ensure your coverage remains adequate and aligns with your current needs. Changes in your life, such as moving to a new location or purchasing a new vehicle, may necessitate adjustments to your coverage.
Regular review of your policy helps prevent costly surprises and ensures you are adequately protected.
Common Exclusions and Limitations
Car insurance policies, while designed to offer comprehensive protection, inevitably contain exclusions and limitations. Understanding these is crucial to avoid disappointment when filing a claim. These restrictions are often in place to manage risk and prevent fraudulent claims, ensuring the long-term viability of the insurance system. It’s vital to carefully review your policy wording to fully grasp what is and isn’t covered.
It’s important to remember that insurance policies are contracts, and the specifics will vary depending on the insurer, the type of policy, and the state in which you reside. This means that while some exclusions are common across the board, others might be unique to your specific agreement. Therefore, always refer to your individual policy documents for definitive information.
Damage Caused by Wear and Tear
Normal wear and tear on your vehicle is generally not covered by car insurance. This includes things like gradual tire degradation, fading paint, or the deterioration of interior components due to age. Insurance is designed to cover unexpected events, not the predictable decline in a vehicle’s condition over time. For example, a cracked windshield caused by a rock chip during driving is typically covered, but a crack caused by years of exposure to the sun is usually not.
Damage from Unpermitted Use
Many policies exclude coverage for damages incurred while using your vehicle for purposes not specified in the policy or against the law. This might include using your car for racing, transporting illegal substances, or operating it while under the influence of alcohol or drugs. A claim for damages sustained during an illegal street race, for example, would likely be denied.
Damage Caused by Intentional Acts
Naturally, car insurance doesn’t cover damage you intentionally cause to your own vehicle or to another’s. This includes acts of vandalism or self-inflicted damage. For instance, if you deliberately scratch your car’s paint, your insurer will not compensate you for the repairs.
Pre-Existing Conditions
Similar to health insurance, pre-existing damage to your vehicle will typically not be covered. If you were aware of damage prior to purchasing your insurance policy and failed to disclose it, any subsequent claim related to that damage is likely to be rejected. This applies to both mechanical and cosmetic issues. For example, if you have a known leak in your engine, any damage resulting from that leak would not be covered.
Failure to Comply with Policy Terms
Many exclusions are tied to the policyholder’s failure to comply with the terms and conditions of their insurance agreement. This can include failing to report an accident promptly, failing to maintain proper vehicle maintenance, or providing false information to the insurer. For example, if you are involved in an accident and fail to notify your insurer within the stipulated timeframe, your claim could be compromised or denied.
Choosing the Right Coverage

Selecting the right car insurance coverage is crucial; it protects you financially in the event of an accident or other unforeseen circumstances. The ideal level of coverage depends on several factors, including your budget, the value of your vehicle, your driving history, and your personal risk tolerance. Understanding your needs and comparing different policy options will help you make an informed decision.
Choosing the appropriate level of coverage involves a careful assessment of your individual circumstances and financial capabilities. Factors such as the age and value of your car, your driving record, and your state’s minimum insurance requirements all play a significant role. Weighing the potential costs of an accident against the premiums for different coverage levels is essential to finding the right balance. It’s also wise to consider the potential consequences of being underinsured.
Factors Influencing Coverage Choice
Several key factors should be considered when choosing your car insurance coverage. These include the value of your vehicle, your driving history, your location, and your financial situation. Higher-value vehicles typically require higher liability coverage limits to adequately protect against potential claims. A clean driving record usually results in lower premiums, while a history of accidents or violations may necessitate higher coverage to offset increased risk. Geographic location also influences premiums, as accident rates vary across regions. Finally, your personal financial resources should be considered; you need to choose coverage that you can comfortably afford while still providing adequate protection.
Comparison of Coverage Levels and Costs
The table below illustrates a comparison of different coverage levels and their associated costs. These are illustrative examples and actual costs will vary based on individual circumstances and location. It’s crucial to obtain personalized quotes from multiple insurers to find the best rates for your specific needs.
| Coverage Level | Liability Coverage (Example) | Collision Coverage (Example) | Comprehensive Coverage (Example) | Estimated Monthly Premium (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum Required | $25,000/$50,000 Bodily Injury, $10,000 Property Damage | Not Included | Not Included | $50 |
| Standard | $100,000/$300,000 Bodily Injury, $50,000 Property Damage | Included with Deductible | Included with Deductible | $100 |
| Premium | $500,000/$1,000,000 Bodily Injury, $100,000 Property Damage | Included with Lower Deductible | Included with Lower Deductible | $150 |
Note: Bodily Injury coverage refers to the maximum amount paid for injuries to others, while Property Damage coverage refers to the maximum amount paid for damage to others’ property. Deductibles represent the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. These figures are purely illustrative and should not be considered as accurate quotes. Always obtain quotes from multiple insurance providers for a comprehensive comparison.
Illustrative Scenarios
Understanding how car insurance policies react in different situations is crucial. Let’s examine two scenarios, one minor and one major, to illustrate the typical response of a standard policy and highlight how different policy types might handle them differently.
Minor Accident Scenario: Fender Bender
Imagine a minor accident where you slightly tap the rear bumper of another car while parking. The damage is minimal – a small scratch on both vehicles, estimated at $500 total. A typical comprehensive and collision insurance policy would cover the repairs to your vehicle, minus your deductible (let’s say $500). Liability coverage would likely cover the other driver’s repair costs, again, potentially after their deductible. If you only had liability coverage, your own vehicle’s repair costs would be your responsibility. If the damage was solely your fault, your insurance premiums may increase slightly in the following year. If it was deemed the other driver’s fault, there would be no impact on your premium.
Major Accident Scenario: Multi-Vehicle Collision
Consider a more serious scenario: a multi-vehicle collision caused by another driver running a red light. Your car sustains significant damage ($10,000), requiring extensive repairs or even replacement. The other driver’s vehicle is also severely damaged, and a passenger in another car suffers injuries requiring medical attention. A comprehensive and collision policy would cover the repairs or replacement of your vehicle, less your deductible. Your liability coverage would help pay for the other driver’s vehicle repairs and the medical bills of the injured passenger, up to your policy limits. Uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage would become relevant if the at-fault driver lacked sufficient insurance to cover all damages. If your policy limits are exceeded, you would be personally responsible for the difference. If you only had liability coverage, you would still be responsible for repairing your vehicle. The absence of collision coverage would leave you responsible for all repair costs to your vehicle. In this instance, the impact on your premium would likely be significant, reflecting the severity of the claim.
Policy Type Differences in Handling Scenarios
The difference in policy types becomes apparent when comparing how they would handle these scenarios. Liability-only coverage would only protect you against claims made against you for damage or injury you caused to others. Comprehensive and collision coverage provides broader protection, covering damage to your own vehicle regardless of fault, adding significant financial security in both scenarios. Uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage is crucial in the major accident scenario, protecting you if the at-fault driver is uninsured or underinsured, a common situation. The higher your policy limits, the greater the protection in both scenarios. The financial consequences of a major accident without sufficient coverage could be devastating.
Concluding Remarks
Choosing the appropriate car insurance policy requires careful consideration of your individual circumstances and risk tolerance. By understanding the various types of coverage available, the factors influencing premiums, and the claims process, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your specific needs. Remember to thoroughly review your policy documents, ask clarifying questions, and always prioritize comprehensive protection. Taking proactive steps to understand your car insurance policy can save you considerable stress and financial burden in the event of an accident or unforeseen circumstances. Armed with knowledge, you can confidently navigate the world of car insurance and secure the best possible coverage.
FAQ Section
What is the difference between liability and collision coverage?
Liability coverage pays for damages you cause to others, while collision coverage pays for damage to your own vehicle regardless of fault.
How often can I expect my car insurance rates to change?
Rates can change annually, or even more frequently, depending on your insurer and any changes in your risk profile (e.g., moving, accidents, tickets).
What happens if I’m involved in an accident and the other driver is uninsured?
Uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage protects you in such scenarios, covering damages to your vehicle and medical expenses.
Can I cancel my car insurance policy at any time?
Yes, but you may incur penalties or cancellation fees depending on your policy terms and the reason for cancellation.
How do I update my information (address, vehicle) on my policy?
Contact your insurance provider directly to update your information. Failure to do so could impact coverage in case of an accident.