The cost of monthly car insurance is a significant financial consideration for most drivers. Understanding the factors that influence premiums is crucial for securing affordable yet comprehensive coverage. This guide delves into the complexities of car insurance pricing, providing insights into how various elements contribute to your monthly bill, empowering you to make informed decisions about your auto insurance.
From the type of vehicle you drive and your driving history to your location and credit score, numerous variables play a role in determining your monthly premium. We’ll explore these factors in detail, offering practical tips and strategies to help you find the best possible coverage at a price that suits your budget. We’ll also guide you through obtaining quotes, understanding policy terms, and saving money on your insurance costs.
Factors Influencing Car Insurance Costs
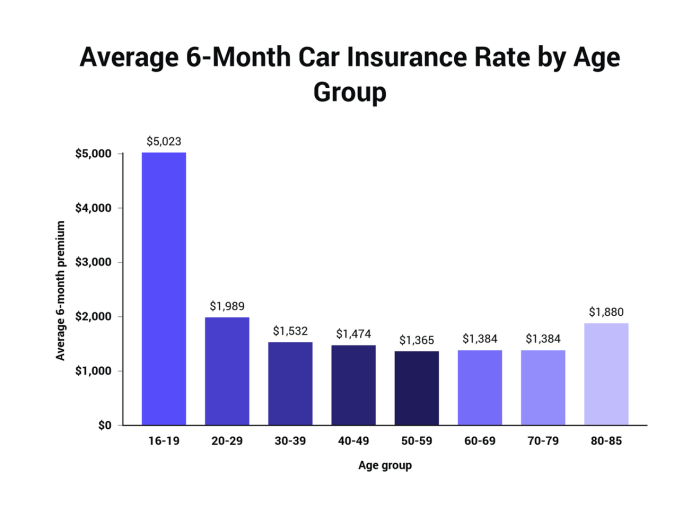
Several key factors significantly impact the monthly cost of car insurance. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions and potentially save money on your premiums. These factors interact in complex ways, so a change in one area can affect the overall cost.
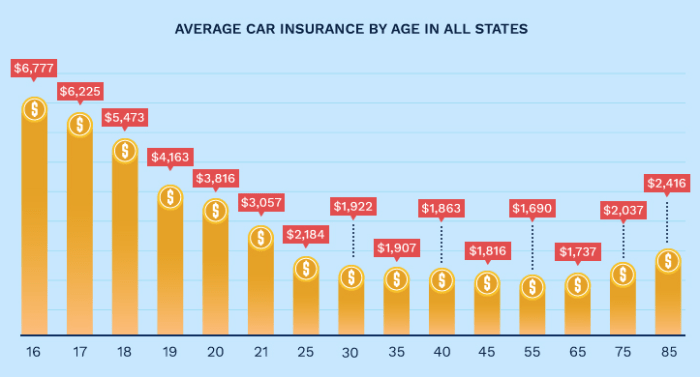
Age
Age is a major determinant of car insurance premiums. Younger drivers, typically those under 25, generally pay higher premiums due to statistically higher accident rates in this age group. Insurance companies perceive them as higher risk. As drivers age and gain experience, their premiums typically decrease, reflecting a lower risk profile. For example, a 20-year-old driver might pay significantly more than a 40-year-old driver with a similar driving record and vehicle. This is because insurance companies use statistical data to assess risk, and younger drivers are statistically more likely to be involved in accidents.
Driving History
A clean driving record is crucial for keeping insurance costs low. Accidents and traffic violations significantly increase premiums. Each accident or ticket adds to your risk profile, leading to higher rates. For instance, a driver with a history of speeding tickets might pay substantially more than a driver with a spotless record. The severity of the accident or violation also plays a role; a serious accident will generally result in a larger premium increase than a minor fender bender. Furthermore, the number of years since the last incident also influences the impact.
Car Type
The type of car you drive directly affects your insurance costs. Sports cars and luxury vehicles are often more expensive to insure than sedans or smaller SUVs. This is because these vehicles are typically more expensive to repair and replace, and they are sometimes associated with a higher risk of accidents. For example, insuring a high-performance sports car will likely cost significantly more than insuring a fuel-efficient compact sedan. The car’s safety features also play a role; vehicles with advanced safety technology might receive lower premiums.
Location
Your location significantly influences your car insurance rates. Areas with higher crime rates, more traffic congestion, and a higher frequency of accidents tend to have higher insurance premiums. Insurance companies consider the risk of theft, vandalism, and accidents in different geographic areas when setting rates. For example, someone living in a densely populated urban area might pay more than someone living in a rural area with lower accident rates. Factors such as the number of uninsured drivers in an area also impact rates.
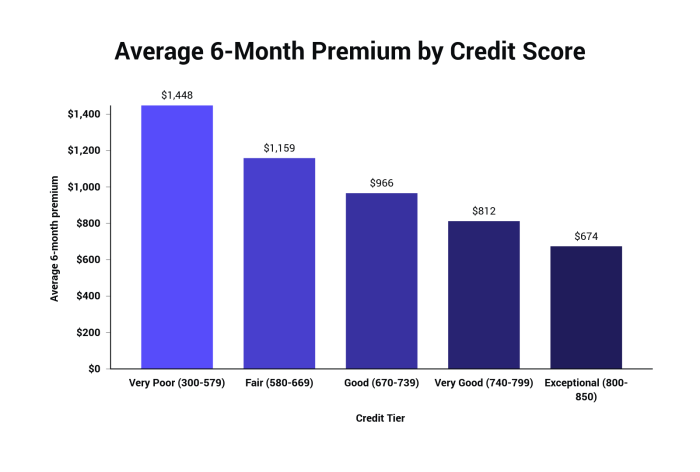
Credit Score
In many states, your credit score is a factor in determining your car insurance premiums. A good credit score typically leads to lower premiums, while a poor credit score can result in significantly higher rates. Insurance companies use credit scores as an indicator of financial responsibility, believing that individuals with good credit are less likely to file fraudulent claims or fail to pay their premiums. For instance, a driver with an excellent credit score might qualify for discounts, whereas a driver with poor credit might face a substantial surcharge.
| Factor | Impact on Cost | Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Younger drivers typically pay more; premiums decrease with age. | A 20-year-old pays more than a 40-year-old with similar driving records. | Higher accident rates for younger drivers lead to higher risk assessments. |
| Driving History | Accidents and tickets significantly increase premiums. | Multiple speeding tickets result in higher premiums than a clean record. | A history of at-fault accidents demonstrates higher risk. |
| Car Type | Sports cars and luxury vehicles are generally more expensive to insure. | A sports car costs more to insure than a sedan. | Higher repair costs and potential for more severe accidents. |
| Location | Areas with higher accident rates and crime have higher premiums. | Urban areas often have higher rates than rural areas. | Insurance companies assess risk based on location-specific data. |
| Credit Score | Good credit often leads to lower premiums; poor credit can result in higher premiums. | Excellent credit score qualifies for discounts; poor credit results in surcharges. | Credit score is used as an indicator of financial responsibility. |
Types of Car Insurance Coverage
Choosing the right car insurance coverage can feel overwhelming, but understanding the different types available is crucial for protecting yourself and your vehicle. This section will Artikel the key types of coverage, highlighting their benefits and limitations. Remember, the specific details and costs will vary depending on your location, insurer, and individual circumstances.
Liability Insurance
Liability insurance covers damages or injuries you cause to others in an accident. This is typically the most basic and legally required type of car insurance. It protects you from financial responsibility for bodily injury or property damage you inflict on another person or their property. For instance, if you cause an accident that results in injuries to another driver and damage to their car, your liability insurance would help cover their medical bills and vehicle repairs. The coverage is usually divided into bodily injury liability and property damage liability, each with its own limits (e.g., $100,000/$300,000 for bodily injury, meaning up to $100,000 per person and $300,000 per accident, and $50,000 for property damage). It’s important to choose limits that reflect your potential risk and financial capacity.
Collision and Comprehensive Insurance
Collision and comprehensive insurance are designed to protect your own vehicle. Collision coverage pays for repairs or replacement of your car if it’s damaged in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. Comprehensive coverage, on the other hand, covers damage to your car caused by events other than collisions, such as theft, vandalism, fire, hail, or falling objects. For example, if a tree falls on your car during a storm, comprehensive insurance would cover the repairs. If you are involved in a collision with another vehicle and are at fault, your collision coverage would cover the repairs to your own vehicle. These coverages are optional but highly recommended to protect your significant investment in a vehicle.
Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage
Uninsured/underinsured motorist (UM/UIM) coverage protects you if you’re involved in an accident caused by a driver who is uninsured or underinsured. Uninsured motorist coverage addresses accidents involving drivers without insurance, while underinsured motorist coverage steps in when the other driver’s liability coverage is insufficient to cover your damages. Consider a scenario where an uninsured driver causes a serious accident resulting in significant medical expenses and vehicle damage; your UM/UIM coverage would help offset those costs. The level of coverage you choose will determine the amount of protection you have in such situations. It is crucial to have adequate UM/UIM coverage, as uninsured drivers are unfortunately a reality on the road.
Personal Injury Protection (PIP)
Personal Injury Protection (PIP) insurance covers medical expenses and lost wages for you and your passengers, regardless of fault. This means that even if you are at fault for an accident, your PIP coverage will help pay for your medical bills and lost income. It can also cover medical expenses for passengers in your vehicle. For example, if you are involved in an accident and suffer injuries, your PIP coverage will help pay for your medical treatment, rehabilitation, and lost wages, even if the other driver is at fault. This coverage offers valuable protection and peace of mind, particularly in states with no-fault insurance systems.
Summary of Key Features
- Liability Insurance: Covers injuries and damages you cause to others. Legally required in most places. Limits are crucial.
- Collision Insurance: Covers damage to your vehicle in an accident, regardless of fault.
- Comprehensive Insurance: Covers damage to your vehicle from non-collision events (theft, vandalism, weather, etc.).
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage: Protects you if you’re hit by an uninsured or underinsured driver.
- Personal Injury Protection (PIP): Covers medical expenses and lost wages for you and your passengers, regardless of fault.
Obtaining Car Insurance Quotes
Securing the best car insurance involves careful comparison shopping. Understanding how to obtain and compare quotes is crucial to finding a policy that meets your needs and budget. This section will guide you through the process of obtaining car insurance quotes, offering tips to maximize your savings and ensure you’re making an informed decision.
Online Quote Acquisition Steps
Obtaining car insurance quotes online is a straightforward process, often involving a few simple steps. Many insurance companies offer online quote tools, providing a convenient way to compare prices and coverage options without leaving your home.
- Visit the insurance company’s website: Navigate to the website of the insurance provider you’re interested in. Most major insurers have user-friendly interfaces designed for quick quote generation.
- Complete the quote form: You’ll be asked to provide information about yourself, your vehicle, and your driving history. This typically includes details such as your age, address, driving record, the year, make, and model of your car, and your desired coverage levels.
- Review and compare quotes: Once you’ve submitted your information, the system will generate a quote outlining the estimated cost of your insurance. Remember to compare quotes from multiple providers to ensure you’re getting the best possible rate.
- Select your coverage: Carefully review the different coverage options available and choose the plan that best suits your needs and budget. Consider factors like your risk tolerance and the value of your vehicle.
- Finalize your purchase: Once you’ve chosen a policy, you can usually complete the purchase online. You’ll need to provide payment information and agree to the terms and conditions of the policy.
Comparing Insurance Quotes Effectively
Comparing quotes from different insurance providers is essential to securing the most competitive price. However, simply focusing on the lowest price isn’t always the best approach. Consider the following factors when comparing quotes:
- Coverage levels: Ensure that the coverage offered matches your needs. A cheaper policy with insufficient coverage could prove costly in the event of an accident.
- Deductibles: A higher deductible will lower your premium, but you’ll pay more out-of-pocket if you make a claim. Consider your financial situation when choosing a deductible.
- Customer service reputation: Research the insurance company’s reputation for customer service. Read reviews and check ratings to gauge their responsiveness and helpfulness.
- Discounts: Inquire about available discounts, such as those for safe driving records, bundling policies, or being a member of certain organizations.
Policy Detail Comprehension Before Purchase
Before committing to a policy, thoroughly review all policy details. Understanding the terms and conditions is vital to avoid unexpected costs or coverage gaps. Pay close attention to the following:
- Coverage limits: Understand the maximum amount the insurer will pay for different types of claims (bodily injury, property damage, etc.).
- Exclusions: Be aware of any situations or events that are not covered by the policy.
- Premium payment options: Determine the available payment methods and frequency (monthly, quarterly, annually).
- Cancellation policy: Understand the terms and conditions for canceling the policy.
Effective Use of Comparison Websites
Comparison websites can streamline the process of obtaining multiple quotes. These websites allow you to enter your information once and receive quotes from various insurers simultaneously. However, remember that the quotes provided are estimates, and the final price may vary slightly depending on the insurer’s underwriting process. It’s advisable to verify the details directly with the insurance provider before making a final decision.
Step-by-Step Guide to Obtaining Car Insurance Quotes
A systematic approach can simplify the process. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Gather necessary information: Collect details about your vehicle, driving history, and desired coverage.
- Use online comparison tools: Utilize comparison websites to receive quotes from multiple insurers.
- Review individual insurer websites: Visit the websites of insurers offering competitive quotes for more detailed information.
- Compare quotes comprehensively: Analyze quotes based on coverage, price, and customer service reputation.
- Contact insurers for clarification: Reach out to insurers with any questions or to verify specific details.
- Choose a policy: Select the policy that best fits your needs and budget.
- Complete the application: Fill out the application and provide the required documentation.
- Pay the premium: Make the initial premium payment to activate your policy.
Wrap-Up
Securing affordable car insurance requires careful planning and understanding of the many factors at play. By carefully considering your driving habits, vehicle type, location, and credit score, and by actively comparing quotes and negotiating with insurers, you can significantly impact your monthly premiums. Remember, informed decision-making is key to obtaining the best possible coverage while managing your expenses effectively. Take control of your car insurance costs and drive with confidence, knowing you have the right protection at the right price.
FAQ Summary
What is the average monthly car insurance cost in the US?
The average monthly cost varies greatly depending on the factors discussed in this guide, but national averages can range from $100 to $200 or more per month.
Can I get car insurance without a driving history?
Yes, but expect higher premiums. Insurers will often use other factors like age and credit score to assess risk.
How often can I change my car insurance policy?
Most insurers allow policy changes or cancellations with proper notice, often 30 days. Check your policy for specifics.
What happens if I get into an accident and don’t have enough coverage?
You could be personally liable for costs exceeding your coverage limits. This could lead to significant financial hardship.
What’s the difference between liability and comprehensive coverage?
Liability covers damage you cause to others. Comprehensive covers damage to your own vehicle from non-collision events (e.g., theft, vandalism).