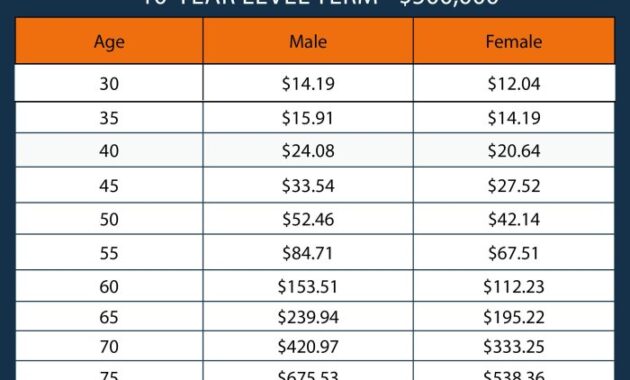
Securing your family’s financial future through life insurance is a crucial step, but understanding the nuances of life term insurance rates can feel overwhelming. This guide dissects the factors influencing these rates, offering clarity and empowering you to make informed decisions. We’ll explore the interplay of age, health, lifestyle, and policy type to provide a comprehensive understanding of how these elements impact your premiums.
From comparing rates across different insurers and policy lengths to identifying strategies for finding affordable coverage, we aim to equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the world of life term insurance with confidence. Understanding these rates is not just about numbers; it’s about securing peace of mind and protecting your loved ones.
Factors Influencing Life Term Insurance Rates
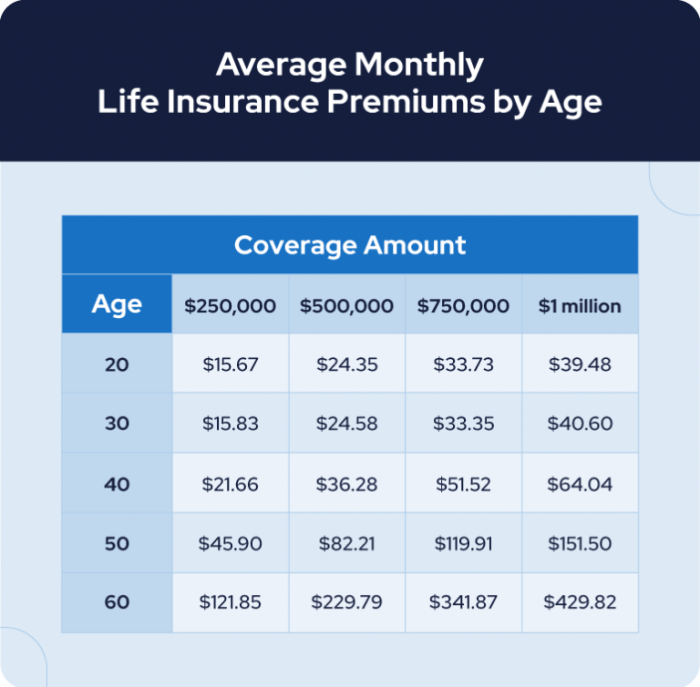
Understanding the factors that determine your life term insurance premiums is crucial for making informed decisions. Several interconnected elements contribute to the final cost, and it’s important to be aware of how these impact your policy. This section will detail these key factors and their influence.
Key Factors Affecting Life Term Insurance Premiums
Several key factors significantly influence the cost of your life term insurance. These factors are intricately linked, and a change in one can affect the others. The following table provides a clear overview:
| Factor | Impact on Premiums | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Increases with age | Older applicants are statistically more likely to pass away during the policy term, leading to higher risk and premiums. | A 30-year-old will generally pay significantly less than a 50-year-old for the same coverage. |
| Health Status | Higher risk = higher premiums | Pre-existing conditions, family history of illness, and current health significantly impact risk assessment. | Someone with a history of heart disease will likely pay more than someone with a clean bill of health. |
| Lifestyle Choices | Unhealthy habits increase premiums | Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and lack of exercise increase the risk of premature death. | Smokers typically pay considerably more than non-smokers for equivalent coverage. |
| Policy Length | Longer term = higher premiums (per year) | Longer-term policies cover a longer period, increasing the insurer’s risk and therefore the overall cost, although the annual premium may be lower. | A 30-year term policy will have a higher total premium than a 10-year term policy, but the annual premium may be lower for the longer term. |
| Gender | Historically, men have paid more | Traditionally, actuarial data showed men having a shorter life expectancy than women. However, this gap is narrowing and regulations are changing to address gender-based pricing disparities. | While historically men paid more, this is subject to change and varies by insurer. |
| Smoking Habits | Smokers pay significantly more | Smoking dramatically increases the risk of various health problems, leading to substantially higher premiums. | A smoker might pay double or even triple the premium of a non-smoker for the same coverage. |
Impact of Age, Health, and Lifestyle on Insurance Costs
Age is a significant factor, as the risk of mortality increases with age. Health status, including pre-existing conditions and family history, plays a crucial role in determining risk. Lifestyle choices, such as smoking, excessive alcohol use, and lack of physical activity, significantly influence the likelihood of developing health problems and, consequently, insurance premiums. Insurers use a complex risk assessment process to evaluate these factors and determine appropriate premiums.
Rate Variations Based on Gender and Smoking Habits
Historically, men have paid higher premiums than women due to differences in life expectancy. However, this disparity is being reassessed by many insurers and regulators due to evolving societal factors. Smoking, regardless of gender, consistently leads to significantly higher premiums due to the increased risk of health complications and premature death. The difference can be substantial, often resulting in premiums double or even triple those of non-smokers.
Impact of Policy Length on Premiums
The length of your term life insurance policy directly impacts the premiums. Longer-term policies (e.g., 30-year) generally have a higher total premium than shorter-term policies (e.g., 10-year) because the insurer assumes a greater risk over a longer period. However, the *annual* premium for a longer-term policy might be lower than for a shorter-term one. The following table illustrates this:
| Policy Length | Annual Premium (Example) | Total Premium |
|---|---|---|
| 10-year | $500 | $5000 |
| 20-year | $400 | $8000 |
| 30-year | $350 | $10500 |
*Note: These are illustrative examples only and actual premiums will vary significantly based on individual circumstances.*
Understanding Policy Types and Their Rates
Choosing the right term life insurance policy depends heavily on understanding the different types available and how their rates vary. This section will explore the key policy types, their cost implications, and factors influencing rate differences between insurers. We will focus on providing a clear comparison to help you make an informed decision.
Several factors contribute to the overall cost of your term life insurance. The type of policy you choose is a significant one, alongside your age, health, lifestyle, and the length of the policy term. Understanding these elements is crucial for securing the best coverage at a price that suits your budget.
Term Life Insurance Policy Types and Rate Comparisons
Term life insurance policies come in various forms, each with its own rate structure. The three most common types are level term, decreasing term, and return of premium. Their key differences are summarized below:
- Level Term: This is the most common type. Your premiums remain constant throughout the policy term. This provides predictable budgeting, making it a popular choice. The death benefit also stays the same during the policy period.
- Decreasing Term: The death benefit gradually decreases over the policy term, while the premiums generally remain level. This type is often less expensive initially but offers diminishing coverage over time. It’s suitable for those needing high coverage initially, such as a mortgage, that decreases over time.
- Return of Premium (ROP): This policy offers a return of all premiums paid if you outlive the policy term. While offering a financial safety net, the premiums are significantly higher than level or decreasing term policies. This is a suitable option for those prioritizing the return of their investment.
Policy Term Length and Cost Implications
The length of your policy term directly impacts the cost of your premiums. Longer terms generally mean higher monthly premiums because the insurance company assumes a greater risk over a longer period. Shorter terms, conversely, result in lower monthly premiums but offer coverage for a shorter duration. The decision hinges on your needs and risk tolerance. For example, a 10-year term policy will have lower premiums than a 20-year term policy, but the coverage ends after 10 years.
Factors Differentiating Rates Between Insurers
Several factors cause rate variations between insurance providers. These include the insurer’s financial strength, claims experience, underwriting guidelines, and the specific benefits offered. Some insurers may have more lenient underwriting requirements, leading to potentially lower rates for individuals with certain health conditions. Others might focus on specific demographics or risk profiles, leading to varying pricing structures. It’s crucial to compare quotes from multiple insurers to find the best rate for your specific circumstances.
Average Rate Comparison Across Insurers
The following table illustrates hypothetical average annual premiums for a healthy 35-year-old male seeking $250,000 in coverage. These figures are for illustrative purposes only and should not be considered a definitive guide. Actual rates vary widely depending on individual circumstances.
| Policy Type | Insurer A | Insurer B | Insurer C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10-Year Level Term | $200 | $225 | $180 |
| 20-Year Level Term | $350 | $400 | $325 |
| 10-Year Decreasing Term | $175 | $190 | $160 |
| 10-Year Return of Premium | $450 | $500 | $425 |
The Role of Health and Lifestyle
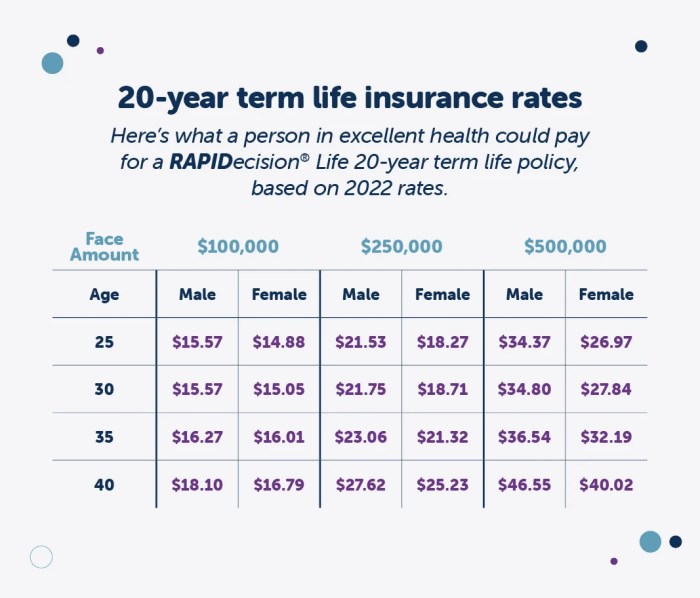
Your health and lifestyle significantly impact your life insurance rates. Insurance companies carefully assess these factors to determine your risk profile, ultimately influencing the premiums you pay. A healthier lifestyle generally translates to lower premiums, while pre-existing conditions or risky behaviors can lead to higher costs. Understanding this relationship empowers you to make informed decisions about your insurance and your well-being.
Impact of Pre-existing Medical Conditions on Life Insurance Rates
Pre-existing medical conditions can substantially affect your life insurance rates. Insurers consider the severity, stability, and potential future costs associated with these conditions. Conditions requiring ongoing treatment or posing a higher risk of mortality typically result in higher premiums. The extent of the rate increase varies depending on the specific condition and the insurer’s underwriting guidelines.
| Pre-existing Condition | Potential Rate Increase (Illustrative Example) |
|---|---|
| High Blood Pressure (well-managed) | 10-20% |
| Type 2 Diabetes (well-managed) | 20-30% |
| Heart Disease | 30-50% or more |
| Cancer (in remission) | Varies significantly based on type and remission status |
*Note: These are illustrative examples only. Actual rate increases can vary significantly depending on the insurer, the specifics of the condition, and other factors.*
Lifestyle Factors Influencing Premium Costs
Several lifestyle factors contribute to your assessed risk profile. These factors are considered alongside your medical history to determine your overall risk and premium.
Your diet, exercise habits, and participation in risky hobbies all play a role. A balanced diet and regular exercise demonstrate a commitment to health, potentially leading to lower premiums. Conversely, a poor diet, lack of exercise, and engaging in high-risk activities (such as skydiving or extreme sports) may result in higher premiums. Smoking is a particularly significant factor, often leading to substantial rate increases.
Insurance Company Assessment of Health Risks
Insurance companies utilize a variety of methods to assess health risks. This often involves reviewing your medical history, conducting a medical examination (sometimes), and requesting lifestyle information through questionnaires. They analyze this data using actuarial models to predict your life expectancy and the likelihood of claiming benefits. This assessment directly influences the premium calculation, with higher-risk individuals paying more.
Positive Lifestyle Changes and Potential Premium Reductions
Making positive lifestyle changes can demonstrably lower your insurance premiums. For example, quitting smoking can significantly reduce your rates over time. Similarly, adopting a healthier diet, engaging in regular exercise, and avoiding risky hobbies can all contribute to a lower risk profile and potentially lower premiums. Some insurers offer discounts or incentives for demonstrating healthy lifestyle choices, further rewarding proactive health management.
Finding Affordable Life Term Insurance
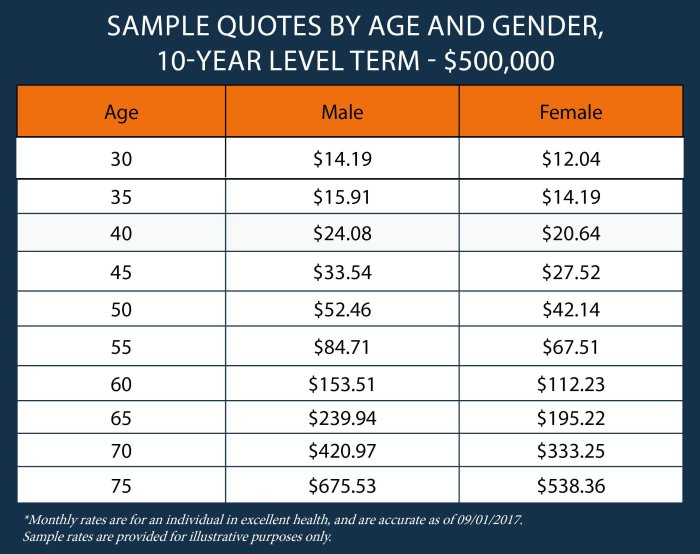
Securing affordable life term insurance is crucial for protecting your loved ones’ financial future without straining your budget. Several strategies can help you find a policy that fits your needs and financial capabilities. Understanding your options and making informed choices is key to finding the right balance between coverage and cost.
Finding the most affordable life term insurance policy requires a proactive and informed approach. It involves careful consideration of several factors, from your health and lifestyle to the type of coverage you need and the insurers you compare.
Strategies for Finding Affordable Life Term Insurance
Several approaches can significantly reduce the cost of your life term insurance premiums. These strategies focus on optimizing your application and shopping around for the best rates.
- Consider a shorter policy term: Shorter term policies (e.g., 10 or 20 years) typically have lower premiums than longer-term or whole life policies. This is because the insurance company’s risk is reduced over a shorter period.
- Increase your deductible or co-pay (if applicable): Similar to health insurance, some life insurance policies may offer options to adjust deductibles or co-pays, which could result in lower premiums. However, this means you’ll pay more out-of-pocket if a claim is filed.
- Improve your health and lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle through diet, exercise, and avoiding risky behaviors can significantly improve your insurability and lead to lower premiums. Insurers often reward healthier applicants with lower rates.
- Shop around and compare quotes: Obtaining quotes from multiple insurers is essential to securing the best possible rate. Different companies use varying underwriting criteria, resulting in diverse pricing structures.
- Consider a higher coverage amount: While counterintuitive, purchasing a higher coverage amount sometimes results in lower premiums per $1,000 of coverage due to economies of scale. This is not always the case, however, and should be considered carefully.
Benefits of Comparing Quotes from Multiple Insurers
Comparing quotes from several insurance providers is a critical step in finding affordable life term insurance. This process ensures you’re not overpaying and allows you to identify the best policy for your individual needs.
By obtaining multiple quotes, you can compare premiums, policy features, and coverage amounts from different companies. This comparative analysis reveals which insurer offers the most competitive pricing for your specific circumstances, ultimately leading to significant savings.
Understanding Policy Terms and Conditions
Before committing to a life insurance policy, thoroughly reviewing the policy’s terms and conditions is paramount. This ensures you fully comprehend the coverage, exclusions, and limitations associated with the policy.
Carefully examine the policy document, paying attention to details such as the definition of covered events, the payout process, and any stipulations or exclusions. Understanding these aspects helps prevent future misunderstandings and ensures you receive the intended benefits.
Step-by-Step Guide to Obtaining and Comparing Life Insurance Quotes
Securing and comparing life insurance quotes effectively requires a structured approach. This methodical process helps you make an informed decision based on accurate information.
- Determine your needs: Assess your financial obligations and determine the appropriate coverage amount needed to protect your family.
- Gather personal information: Collect necessary personal data, including your age, health history, and lifestyle information.
- Obtain quotes from multiple insurers: Use online comparison tools or contact insurers directly to request quotes. Provide accurate information to ensure accurate rate calculations.
- Compare quotes side-by-side: Create a spreadsheet or use a comparison tool to analyze premiums, coverage amounts, policy terms, and other relevant factors.
- Review policy documents carefully: Before making a decision, thoroughly review the policy documents of your top choices to understand the details and exclusions.
- Choose a policy: Select the policy that best meets your needs and budget, considering the balance between coverage, cost, and policy terms.
Illustrative Examples of Rate Variations
Life insurance premiums are not a one-size-fits-all proposition. Numerous factors influence the final cost, creating significant variations between individuals. Understanding these variations is crucial for making informed decisions about life insurance coverage. This section will illustrate how different factors combine to impact premiums using hypothetical scenarios and demonstrate the potential for cost savings through lifestyle changes and policy adjustments.
Rate Differences Based on Age, Health, and Habits
The following table illustrates the potential premium differences between two hypothetical individuals applying for a $500,000, 20-year term life insurance policy.
| Factor | Individual A (30-year-old, Healthy Non-Smoker) | Individual B (50-year-old, Smoker with Pre-existing Condition) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 30 | 50 |
| Health Status | Excellent | Fair (High Blood Pressure) |
| Smoking Status | Non-smoker | Smoker |
| Estimated Annual Premium | $500 | $2000 |
This hypothetical example demonstrates a significant difference in premiums. Individual A, being younger, healthier, and a non-smoker, receives a much lower rate. Individual B’s older age, smoking habit, and pre-existing condition significantly increase their premium. These differences highlight the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle and applying for insurance at a younger age. It is important to note that these are hypothetical figures and actual premiums will vary depending on the specific insurer and policy details.
Cost Savings from Healthier Lifestyle Choices
Adopting a healthier lifestyle can lead to significant long-term cost savings on life insurance. For example, quitting smoking can reduce premiums substantially within a few years as insurers reassess risk. Similarly, managing pre-existing conditions like high blood pressure through medication and lifestyle changes can improve health status, leading to lower premiums over time. These savings accumulate over the life of the policy, resulting in considerable financial benefits. Some insurers even offer discounts for participating in wellness programs or achieving health milestones.
Impact of Policy Term Length on Overall Cost
The length of the policy term significantly impacts the overall cost of coverage. Shorter-term policies (e.g., 10-year term) generally have lower annual premiums than longer-term policies (e.g., 30-year term). However, the total premium paid over the life of the policy might be lower for a longer-term policy if the premiums remain relatively stable. Conversely, if health status deteriorates significantly over time, renewing a shorter-term policy could result in higher premiums in the future. The optimal policy term depends on individual circumstances and financial goals, requiring careful consideration of the trade-offs between immediate cost and long-term coverage.
Last Point
Navigating the complexities of life term insurance rates requires careful consideration of numerous factors. By understanding the influence of age, health, lifestyle, and policy type, you can make informed choices that align with your financial goals and family’s needs. Remember, comparing quotes from multiple insurers and proactively managing your health are key steps in securing affordable and appropriate coverage. This proactive approach ensures you not only obtain the necessary protection but also optimize your premiums for long-term financial well-being.
General Inquiries
What is the difference between level term and decreasing term life insurance?
Level term insurance provides a fixed death benefit throughout the policy term, while decreasing term insurance offers a death benefit that gradually declines over time.
How often are life insurance rates reviewed and adjusted?
Rates are generally reviewed periodically by insurance companies, but the frequency varies. Significant changes in mortality rates or other risk factors can trigger adjustments.
Can I change my life insurance policy after it’s been issued?
Some policies allow for changes, such as increasing coverage, but this often involves a new underwriting process and may result in higher premiums. Check your policy’s terms and conditions.
What happens if I miss a premium payment?
Missing a payment can lead to a lapse in coverage. Most insurers offer grace periods, but it’s crucial to contact them immediately to avoid policy cancellation.
Does my credit score affect my life insurance rates?
While not a direct factor in all states, your credit score can sometimes influence the rates offered, particularly for certain insurers.