Navigating the world of healthcare can feel like deciphering a complex code, especially when it comes to understanding your medical insurance options. One common type of plan, the Preferred Provider Organization (PPO), offers flexibility but also presents a unique set of considerations. This guide unravels the intricacies of PPO medical insurance, empowering you to make informed decisions about your healthcare coverage.
We’ll explore the core features of PPO plans, comparing them to other common options like HMOs and POS plans. Understanding terms like deductible, copay, and coinsurance is crucial for managing your healthcare costs effectively. We’ll also delve into the process of choosing a plan, considering factors like network size, provider availability, and premium costs, ultimately guiding you towards selecting a PPO plan that best aligns with your individual needs and budget.
Defining PPO Medical Insurance
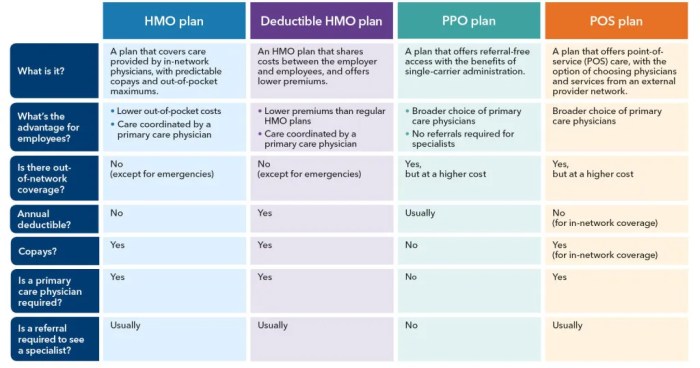
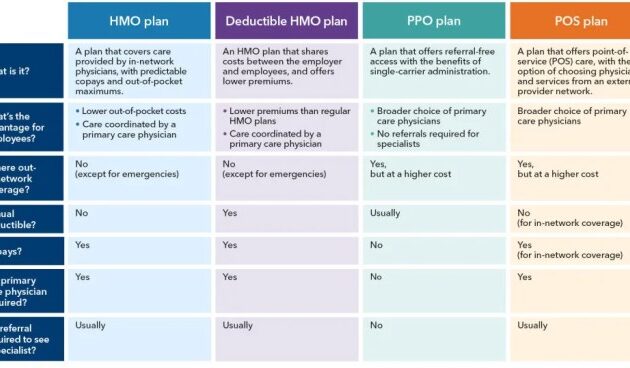
PPO, or Preferred Provider Organization, plans are a common type of medical insurance in the United States. They offer a balance between flexibility and cost, making them a popular choice for many individuals and families. Understanding the key features of a PPO plan is crucial for making informed decisions about your healthcare coverage.
Core Features of PPO Medical Insurance Plans
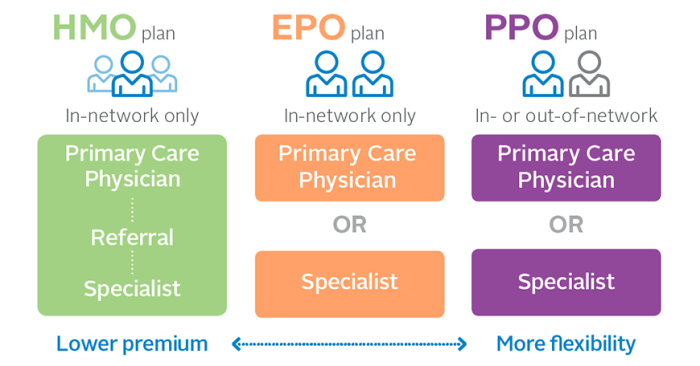
PPO plans allow you to see any doctor or specialist, in-network or out-of-network, without needing a referral. However, you’ll generally pay less if you stick to the plan’s network of preferred providers. This network consists of doctors, hospitals, and other healthcare facilities that have negotiated discounted rates with the insurance company. The flexibility to see out-of-network providers is a significant advantage for many, although it comes with higher costs. Another key feature is the absence of a primary care physician (PCP) gatekeeper; you’re free to choose specialists directly.
Differences Between PPO and Other Insurance Types
PPO plans differ significantly from other types of health insurance, such as HMOs (Health Maintenance Organizations) and POS (Point of Service) plans. HMO plans typically require you to choose a PCP who acts as a gatekeeper, referring you to specialists within the network. Seeing out-of-network providers is usually not covered, or only covered under very limited circumstances. POS plans offer a hybrid approach, allowing you to see out-of-network providers but generally at a higher cost. The key differentiator is the level of flexibility and the cost implications associated with seeing in-network versus out-of-network providers.
Common Terminology Associated with PPO Plans
Several key terms are commonly associated with PPO plans. Understanding these terms is essential for navigating your plan and understanding your financial responsibility for healthcare services.
- Deductible: The amount you must pay out-of-pocket for covered healthcare services before your insurance company begins to pay. For example, a $1,000 deductible means you’ll pay the first $1,000 of your medical bills yourself.
- Copay: A fixed amount you pay for a covered healthcare service, such as a doctor’s visit. Copays are typically lower for in-network providers.
- Coinsurance: Your share of the costs of a covered healthcare service, calculated as a percentage of the allowed amount after you’ve met your deductible. For instance, 20% coinsurance means you pay 20% of the bill after the deductible is met.
- Out-of-Pocket Maximum: The most you’ll pay out-of-pocket for covered healthcare services in a plan year. Once you reach this limit, your insurance company covers 100% of the costs for covered services.
Comparison of PPO Plans from Three Major Insurance Providers
The following table compares sample PPO plans from three major insurance providers. Note that these are examples only, and actual plans and costs will vary depending on location, coverage level, and other factors.
| Provider | Deductible | Copay (Office Visit) | Out-of-Pocket Maximum (Individual) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Provider A | $2,000 | $50 | $6,000 |
| Provider B | $1,500 | $40 | $5,000 |
| Provider C | $3,000 | $60 | $7,500 |
Choosing a PPO Plan
Selecting the right PPO (Preferred Provider Organization) medical insurance plan can significantly impact your healthcare experience and financial well-being. Understanding the key factors involved in the decision-making process is crucial to finding a plan that best suits your individual needs and budget. This section will guide you through the process of choosing a PPO plan that aligns with your healthcare requirements.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a PPO Plan
Several key factors influence the suitability of a PPO plan. Carefully evaluating these aspects will ensure you choose a plan that offers the best balance of coverage, cost, and convenience.
- Network Size: A larger network generally provides more choices of doctors and hospitals. Consider whether you prefer a broad network offering greater flexibility or a smaller, more focused network that may offer more specialized care within a specific geographic area.
- Provider Availability: Verify that your preferred doctors and specialists are included in the plan’s network. Checking the provider directory online is essential before making a decision. A seemingly inexpensive plan is useless if your preferred physician is out of network.
- Premium Costs: Premiums are the monthly payments you make for your insurance coverage. Compare premium costs across different plans, keeping in mind that lower premiums might mean higher out-of-pocket expenses.
- Deductibles and Coinsurance: The deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage begins. Coinsurance is the percentage of costs you share with your insurer after meeting your deductible. Lower deductibles and coinsurance usually result in higher premiums.
- Out-of-Pocket Maximum: This is the most you will pay out-of-pocket in a given year. Once this limit is reached, your insurance covers 100% of eligible expenses. A lower out-of-pocket maximum offers greater financial protection.
Strategies for Comparing PPO Plans from Different Providers
Effectively comparing PPO plans requires a systematic approach. Using online comparison tools and directly contacting insurance providers can significantly aid in this process.
- Use Online Comparison Tools: Many websites allow you to input your criteria (location, age, desired coverage) and compare plans from different providers side-by-side. This facilitates a quick overview of various options.
- Contact Insurance Providers Directly: Supplement online comparisons by contacting insurance providers directly to clarify any ambiguities or obtain additional information about specific plan features.
- Review Plan Documents Carefully: Don’t rely solely on summaries; carefully review the complete plan documents to understand all aspects of coverage, including exclusions and limitations.
- Consider Long-Term Healthcare Needs: Think about your anticipated healthcare needs over the plan’s duration. For example, if you anticipate needing specialized care, ensure the plan includes access to those specialists.
Understanding Your Healthcare Needs Before Selecting a Plan
A thorough assessment of your individual healthcare needs is paramount in selecting a suitable PPO plan. This involves considering your current health status, anticipated future needs, and preferred healthcare providers.
For example, a person with a chronic condition requiring frequent specialist visits would prioritize a plan with extensive coverage for that specialty and a lower out-of-pocket maximum. Conversely, a healthy individual might opt for a plan with a higher deductible and lower premiums, assuming a lower likelihood of significant healthcare expenses.
Decision-Making Flowchart for Choosing a PPO Plan
The following flowchart Artikels a step-by-step process for selecting a PPO plan.
[Flowchart Description:] The flowchart would begin with a “Start” box. The next box would be “Assess your healthcare needs and budget.” This would branch into two boxes: “High healthcare needs/budget” and “Low healthcare needs/budget.” The “High healthcare needs/budget” branch would lead to a box indicating to prioritize plans with low deductibles, low out-of-pocket maximums, and comprehensive coverage. The “Low healthcare needs/budget” branch would lead to a box suggesting prioritizing plans with lower premiums and higher deductibles. Both branches would then converge to a box: “Compare plans using online tools and provider websites.” This leads to a box: “Review plan documents carefully.” The final box would be “Choose the best plan” followed by an “End” box.
Understanding PPO Costs and Coverage
Choosing a PPO plan involves understanding the financial implications. While offering flexibility, PPOs utilize a system of deductibles, copays, and coinsurance to determine your out-of-pocket expenses. This section clarifies these cost-sharing mechanisms and provides strategies to manage healthcare costs effectively.
Deductibles, Copays, and Coinsurance
Deductibles, copays, and coinsurance are key components of most PPO plans. The deductible is the amount you must pay out-of-pocket for covered healthcare services before your insurance begins to pay. A copay is a fixed amount you pay for a specific medical service, such as a doctor’s visit. Coinsurance is your share of the costs of a covered healthcare service, calculated as a percentage after you’ve met your deductible. For example, a plan might have a $1,000 deductible, a $50 copay for doctor visits, and 20% coinsurance for other covered services. If you have a $5,000 surgery after meeting your deductible, you would pay 20% of the remaining $4,000, or $800.
Examples of Medical Procedures and Associated Costs
The cost of medical procedures under a PPO plan varies significantly based on the procedure, the provider, and the specific plan. A routine checkup might cost a few hundred dollars including the copay, while a major surgery could cost tens of thousands, even after insurance coverage. For instance, a simple appendectomy could range from $5,000 to $15,000 depending on factors such as hospital stay length and complications. Prescription drugs also vary widely in cost, with brand-name medications generally more expensive than generic alternatives. A specialist visit will typically have a higher copay than a general practitioner visit. It’s crucial to check your plan’s specific coverage details and provider networks for accurate cost estimations.
Strategies for Minimizing Healthcare Expenses with a PPO Plan
Managing healthcare costs with a PPO plan requires proactive planning and informed decision-making. Understanding your plan’s benefits, choosing in-network providers, and utilizing preventive care are key elements in controlling expenses.
- Choose In-Network Providers: Using in-network providers ensures lower costs compared to out-of-network care. Your plan will typically reimburse a higher percentage of the cost when using in-network providers.
- Utilize Preventive Care: Preventive services, such as annual checkups and screenings, are often covered at little to no cost, helping to detect potential problems early and avoid more expensive treatments later.
- Negotiate Medical Bills: Don’t hesitate to negotiate medical bills. Hospitals and providers are often willing to work with patients to create payment plans or reduce outstanding balances.
- Shop Around for Prescription Drugs: Compare prices at different pharmacies and consider using generic medications when possible to reduce prescription drug costs.
- Review Your Explanation of Benefits (EOB): Carefully review your EOB statements to ensure accuracy and identify any potential errors or discrepancies.
- Consider a Health Savings Account (HSA): If your PPO plan is HSA-eligible, contributing to an HSA can provide tax advantages and help you save for future medical expenses.
Using Your PPO Plan Effectively
Maximizing the benefits of your PPO plan requires understanding how to navigate its features and processes. This section will guide you through key aspects of using your PPO plan effectively, from finding in-network providers to understanding your Explanation of Benefits (EOB) statement.
Finding In-Network Doctors and Specialists
Locating in-network healthcare providers is crucial for minimizing out-of-pocket costs. Most PPO plans offer online provider directories accessible through their member website or mobile app. These directories allow you to search for doctors and specialists by specialty, location, and even language spoken. You can also contact your insurance provider’s customer service department for assistance in finding in-network providers in your area. It’s advisable to verify a provider’s in-network status before your appointment to avoid unexpected billing. For example, you might search for “cardiologist” and your zip code, and the directory will list all in-network cardiologists within a specific radius.
Filing a Claim with a PPO Insurance Provider
While many PPO plans handle claims automatically through electronic billing with in-network providers, you may need to file a claim yourself for out-of-network services or certain situations. The process typically involves completing a claim form, which you can usually download from your insurer’s website. This form will require information such as your policy number, the date of service, the provider’s information, and a detailed description of the services rendered. Supporting documentation, such as receipts or bills, will also be needed. Submitting your claim can be done through mail, fax, or online portals, depending on your insurance provider’s preferences. Always retain copies of all submitted documents for your records. For instance, if you receive treatment from an out-of-network provider for an emergency, you would file a claim with the necessary documentation to receive reimbursement.
The Importance of Preventative Care Under a PPO Plan
PPO plans often cover preventative care services at little to no cost. These services, such as annual checkups, vaccinations, and screenings, are designed to detect potential health issues early and prevent more serious conditions from developing. Taking advantage of these preventative services can lead to better long-term health outcomes and reduce healthcare costs down the line. For example, a yearly physical exam may identify a potentially serious issue early, preventing the need for more extensive and costly treatment later. Regular screenings, such as mammograms or colonoscopies, can also detect conditions early, when treatment is often more successful.
Interpreting an Explanation of Benefits (EOB) Statement
Your Explanation of Benefits (EOB) statement is a summary of the healthcare services you received and how your insurance plan covered those services. Understanding your EOB is crucial for monitoring your healthcare expenses and ensuring accurate billing. The statement will typically include details such as the date of service, the provider’s name, the services rendered, the charges billed, the amount your insurance paid, and your remaining responsibility (copay, coinsurance, or deductible). It will also often show the allowed amount (the amount your insurance plan considers reasonable and customary for a given service), helping you understand any discrepancies between the billed amount and the payment made. For example, if the billed amount is $100, but the allowed amount is $80, your insurance may only pay $80, and you may be responsible for the remaining $20. Reviewing your EOB carefully for any errors or inconsistencies is essential.
Potential Drawbacks of PPO Plans
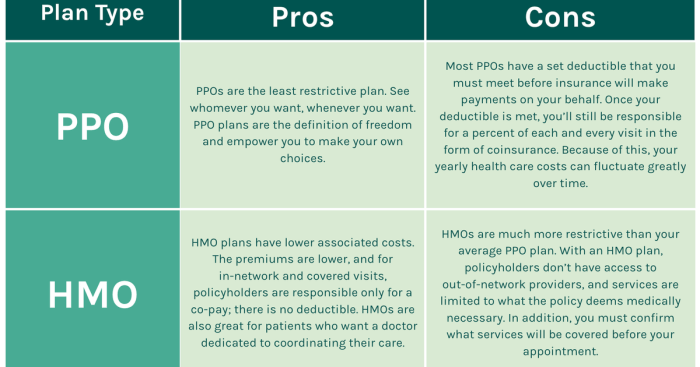
While PPO plans offer flexibility and broad access to healthcare providers, they also come with potential downsides that prospective buyers should carefully consider. Understanding these drawbacks is crucial for making an informed decision about the best health insurance plan for your individual needs and financial situation. Comparing PPOs to other plan types like HMOs and EPOs reveals a nuanced picture of cost and access trade-offs.
Higher Premiums and Out-of-Pocket Costs
PPO plans often have higher monthly premiums than HMOs or other more restrictive plans. This is because PPOs offer greater choice and convenience, which translates to higher administrative costs for the insurance company. Furthermore, while PPOs typically have higher out-of-pocket maximums than HMOs, the lack of a gatekeeper physician and the freedom to choose specialists without referrals can lead to higher overall out-of-pocket expenses if you utilize many services. For example, a patient needing extensive specialist care might find their total cost higher with a PPO despite the higher out-of-pocket maximum, due to accumulating costs before reaching that maximum.
Cost-Effectiveness Compared to Other Options
The cost-effectiveness of a PPO varies greatly depending on individual healthcare needs and utilization. For individuals who require frequent specialist visits or extensive testing, the lack of referral requirements in a PPO could lead to significantly higher out-of-pocket costs compared to an HMO, where a primary care physician manages referrals and helps control utilization. Conversely, a healthy individual with minimal healthcare needs might find a PPO’s flexibility less valuable and its higher premiums a disadvantage compared to a less expensive HMO or EPO. A person with a chronic condition requiring consistent specialized care might find the convenience of a PPO worthwhile, even if the overall cost is higher, while someone with infrequent, routine care might find a less expensive plan more suitable.
Illustrative Cost Comparison: PPO vs. HMO
Imagine two hypothetical patients, Sarah and John, both needing knee surgery. Sarah has a PPO plan with a $10,000 annual out-of-pocket maximum and a $500 monthly premium. John has an HMO plan with a $5,000 annual out-of-pocket maximum and a $300 monthly premium. Sarah chooses her surgeon, incurring costs totaling $8,000. John, needing a referral from his PCP, sees an in-network surgeon and pays $4,000. While John’s out-of-pocket expenses are lower, Sarah’s greater flexibility may have been worth the extra cost to her. The cost difference, however, becomes more significant if both patients require additional follow-up care, potentially exceeding their respective out-of-pocket maximums. This illustrates that cost-effectiveness depends heavily on individual circumstances and healthcare utilization.
Summary
Choosing a medical insurance PPO plan requires careful consideration of various factors, from network size and provider availability to the financial implications of deductibles, copays, and coinsurance. By understanding the nuances of PPO plans and employing effective cost-saving strategies, you can navigate the healthcare system with greater confidence and control. Remember, proactive planning and a thorough understanding of your chosen plan are key to maximizing its benefits and minimizing unexpected expenses. This guide serves as a foundation for your journey toward informed healthcare decision-making.
Questions and Answers
What is the difference between an in-network and out-of-network provider in a PPO plan?
In-network providers are doctors and specialists who have contracted with your insurance company to provide services at a negotiated rate. Using in-network providers generally results in lower out-of-pocket costs. Out-of-network providers haven’t contracted with your insurer; using them typically leads to higher costs.
Can I see a specialist without a referral under a PPO plan?
Yes, generally, PPO plans do not require referrals to see specialists. This offers greater flexibility in choosing your healthcare providers.
How do I file a claim with my PPO insurance provider?
The process varies by provider, but generally involves submitting a claim form with supporting documentation (like receipts and medical bills) either online, via mail, or through your provider’s mobile app.
What is an Explanation of Benefits (EOB)?
An EOB is a statement from your insurance company summarizing the services provided, the charges incurred, the amounts paid by the insurance company, and your remaining responsibility.