
Securing adequate insurance is a crucial aspect of life in New Jersey, a state with a diverse population and a range of potential risks. Understanding the intricacies of the New Jersey insurance market, from the major players to the specific regulations, is essential for both individuals and businesses. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of New Jersey insurance companies, offering insights into the types of coverage available, premium comparisons, consumer protection, and the impact of natural disasters. We aim to equip you with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions about your insurance needs.
From the historical foundations of prominent New Jersey-based insurers to the latest technological advancements shaping the industry, we explore the key aspects that influence the cost and availability of insurance in the Garden State. We’ll examine the role of regulatory bodies, discuss the impact of factors like location and driving history on premiums, and highlight the importance of understanding your policy’s coverage and limitations.
Top New Jersey Insurance Companies
New Jersey’s insurance market is robust and competitive, with a diverse range of companies offering various products and services. Understanding the major players and their history provides valuable insight into the state’s economic landscape and the evolution of the insurance industry. This section details some of the leading insurance companies operating within New Jersey, focusing on their market presence, primary lines of business, and historical context.
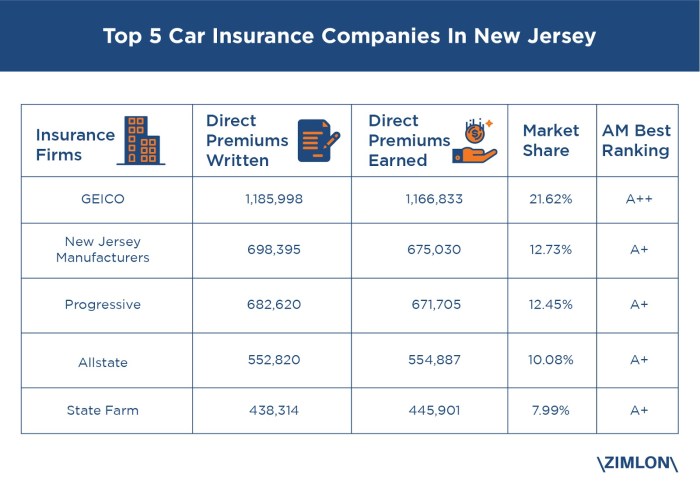
Ten Largest Insurance Companies in New Jersey
Determining precise market share rankings for insurance companies requires access to proprietary data, which is often not publicly available. However, based on publicly available information such as revenue, number of policies, and general market presence, we can identify ten prominent insurance companies operating extensively in New Jersey. This list is not an official ranking by market share, but rather a representation of significant players in the New Jersey insurance market. The precise ranking fluctuates based on annual reports and market dynamics.
| Rank | Company Name | Primary Lines of Business | Year Founded |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | State Farm | Auto, Home, Life | 1922 |
| 2 | Allstate | Auto, Home, Life | 1931 |
| 3 | Geico | Auto, Home | 1936 |
| 4 | Liberty Mutual | Auto, Home, Commercial | 1912 |
| 5 | Progressive | Auto, Home | 1937 |
| 6 | USAA | Auto, Home, Life | 1922 |
| 7 | Farmers Insurance | Auto, Home | 1928 |
| 8 | Nationwide | Auto, Home, Life | 1926 |
| 9 | AAA | Auto, Home | 1902 |
| 10 | Chubb | Commercial, Personal Lines | 1882 |
History of Prominent New Jersey-Based Insurance Companies
While many large national insurers operate extensively in New Jersey, fewer are headquartered there. This section highlights the founding and early history of three prominent companies with significant New Jersey presence, illustrating the evolution of the insurance industry within the state. Note that detailed historical information may require further research into company archives and historical records.
Further research into specific company archives would be needed for a more comprehensive historical analysis.
Types of Insurance Offered in New Jersey

New Jersey residents and businesses have access to a wide range of insurance options, each designed to protect against specific risks. Understanding the different types of insurance available and the regulatory framework governing them is crucial for making informed decisions about coverage. This section details the common types of insurance offered in New Jersey, including their specific requirements and key differences.
New Jersey’s Department of Banking and Insurance plays a significant role in regulating the insurance industry within the state, ensuring consumer protection and maintaining market stability. The specific requirements and regulations vary depending on the type of insurance.
Auto Insurance
Auto insurance is mandatory in New Jersey, protecting drivers and their vehicles against financial losses resulting from accidents. The state mandates minimum coverage levels for bodily injury and property damage liability. Policies often include additional coverage options like collision, comprehensive, uninsured/underinsured motorist, and medical payments. The New Jersey Department of Banking and Insurance sets specific standards for policy language and claims handling.
Key differences between auto insurance policies lie primarily in the coverage limits and the inclusion of optional coverages. A higher liability limit provides greater protection in case of a serious accident. Collision coverage repairs or replaces your vehicle after an accident regardless of fault, while comprehensive coverage protects against non-collision events such as theft or vandalism.
Homeowners Insurance
Homeowners insurance protects against financial losses associated with damage to a home and its contents. Coverage typically includes dwelling protection, personal property coverage, liability protection, and additional living expenses. The specific coverage amounts and policy terms are negotiated between the homeowner and the insurance company. New Jersey regulations mandate certain disclosure requirements and standards for claims handling.
The key differences between homeowners insurance policies stem from coverage amounts and deductibles. A higher coverage amount provides greater protection against significant losses, while a higher deductible reduces the premium but increases the out-of-pocket expense in case of a claim. The type of construction and location of the property also significantly influence the premium.
Health Insurance
Health insurance in New Jersey is largely governed by the Affordable Care Act (ACA). The ACA established health insurance marketplaces where individuals and families can purchase health plans that meet minimum essential coverage requirements. New Jersey also offers its own state-based marketplace. Regulations cover aspects like pre-existing conditions, essential health benefits, and affordability standards.
Key differences between health insurance plans relate to cost-sharing, such as deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket maximums. Network size and provider choices also vary significantly. Different plans offer different levels of coverage for specific services, such as prescription drugs and mental health care.
Life Insurance
Life insurance provides financial protection to beneficiaries upon the death of the insured. Various types of life insurance exist, including term life, whole life, and universal life insurance. Each type offers different features, benefits, and premium structures. New Jersey regulations govern the disclosure of policy information and the solvency of insurance companies.
The key difference between life insurance policies is the duration of coverage and the cash value accumulation. Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period, while whole life insurance provides lifelong coverage and cash value accumulation. Universal life insurance offers flexibility in premium payments and death benefit amounts.
Commercial Insurance
Commercial insurance protects businesses against various risks, including property damage, liability claims, and business interruption. Types of commercial insurance include general liability, commercial auto, workers’ compensation, and professional liability insurance. New Jersey regulations govern the minimum coverage requirements and the claims handling procedures for each type of commercial insurance.
Key differences between commercial insurance policies include the specific types of risks covered, the coverage limits, and the premium costs. The size and nature of the business, its location, and its industry significantly influence the type and cost of commercial insurance needed.
Comparing Insurance Premiums in New Jersey
Understanding insurance premiums in New Jersey is crucial for residents seeking the best value for their coverage. Premiums vary significantly based on several interconnected factors, leading to a wide range of costs across the state. This section will delve into the factors affecting premium costs and provide a comparison of average premiums across different regions and insurance types.
Average Auto Insurance Premiums Across New Jersey Counties
Auto insurance premiums in New Jersey exhibit considerable variation across its 21 counties. Several factors contribute to these differences, including accident rates, population density, and the average cost of vehicle repairs. Generally, counties with higher accident rates and denser populations tend to have higher premiums. For example, counties surrounding major metropolitan areas like Essex and Hudson often see higher premiums than more rural counties. Precise figures fluctuate yearly due to insurance company adjustments and market dynamics, and obtaining exact county-level averages requires consulting multiple insurance company databases or specialized industry reports. However, a general trend of higher premiums in urban and suburban areas compared to rural areas consistently emerges.
Factors Influencing Insurance Premium Costs
Numerous factors influence the final cost of insurance premiums. These can be broadly categorized into driver-related factors, vehicle-related factors, and location-related factors.
Driver-related factors include driving history (accidents, violations), age and driving experience (younger, inexperienced drivers typically pay more), and credit score (a higher credit score often correlates with lower premiums). Vehicle-related factors involve the make, model, and year of the vehicle (newer, more expensive vehicles often command higher premiums), safety features (vehicles with advanced safety features might receive discounts), and vehicle usage (business use generally leads to higher premiums than personal use). Location-related factors encompass the specific address of the insured, considering factors like crime rates, accident frequency in the area, and the overall cost of repairs in the region.
Comparative Table of Average Premiums in Major New Jersey Cities
The following table presents estimated average annual premiums for auto and home insurance in three major New Jersey cities. It is important to note that these are averages and individual premiums can vary significantly based on the factors discussed previously. The data presented is illustrative and should not be considered definitive. Actual premiums should be obtained through direct quotes from insurance providers.
| City | Average Annual Auto Insurance Premium | Average Annual Homeowners Insurance Premium |
|---|---|---|
| Newark | $1800 – $2500 | $1500 – $2200 |
| Jersey City | $1700 – $2400 | $1400 – $2100 |
| Trenton | $1500 – $2000 | $1200 – $1800 |
Consumer Protection and Regulations
Navigating the insurance landscape in New Jersey requires understanding the robust consumer protection measures in place. The state actively works to ensure fair practices and protect policyholders from unethical or unfair treatment by insurance companies. This involves a dedicated regulatory body and several key laws designed to safeguard your rights.
The New Jersey Department of Banking and Insurance (DOBI) plays a central role in overseeing the insurance industry within the state.
The Role of the New Jersey Department of Banking and Insurance (DOBI)
The DOBI is the primary regulatory agency responsible for licensing and supervising insurance companies operating in New Jersey. Its responsibilities encompass a wide range of activities, including ensuring the solvency of insurance companies, monitoring their compliance with state laws and regulations, investigating consumer complaints, and educating the public about insurance-related matters. The DOBI’s authority extends to all aspects of the insurance market, from setting minimum coverage requirements to mediating disputes between insurers and policyholders. They conduct regular audits and investigations to maintain market integrity and protect consumer interests. Their website serves as a valuable resource for information on insurance regulations, company licensing, and consumer rights.
Key Consumer Protection Laws and Regulations
Several key laws and regulations are designed to protect New Jersey consumers. These include provisions that mandate fair claims practices, prevent unfair discrimination in underwriting and pricing, and provide avenues for resolving disputes. Examples of such legislation include regulations concerning the timely processing of claims, the prohibition of unfair claim settlement practices, and requirements for clear and understandable policy language. The New Jersey Consumer Fraud Act also provides additional protection against deceptive or fraudulent insurance practices.
Filing Complaints and Seeking Assistance
Consumers facing insurance-related issues have several avenues for redress. The DOBI offers a formal complaint process through which policyholders can report concerns regarding unfair claims handling, deceptive sales practices, or other violations of state regulations. The complaint process typically involves submitting a detailed account of the issue, supporting documentation, and contact information. The DOBI then investigates the complaint, contacts the involved insurance company, and works to resolve the matter. In addition to filing a formal complaint with the DOBI, consumers may also seek assistance from consumer advocacy groups or legal professionals specializing in insurance law. These resources can provide guidance and representation in navigating complex insurance disputes. For example, the New Jersey Association of Realtors often provides resources and information for its members regarding real estate-related insurance matters. Many legal aid organizations also offer assistance to consumers facing insurance-related problems.
Impact of Natural Disasters on Insurance

New Jersey’s coastal location and susceptibility to severe weather events make it particularly vulnerable to natural disasters. These events significantly impact the insurance industry, leading to increased claims, adjusted risk assessments, and changes in policy offerings. Understanding this impact is crucial for both insurers and residents of the state.
The frequency and severity of hurricanes, floods, and nor’easters in New Jersey directly correlate with the volume of insurance claims filed. Major storms result in widespread property damage, necessitating extensive payouts from insurance companies. This can lead to increased premiums for policyholders to offset the increased risk and potential losses for insurers. The financial burden on insurance companies can be substantial, especially during years with multiple significant events.
Hurricane and Flood Insurance Claims
Hurricanes and floods are the most significant natural disaster threats to New Jersey. Hurricanes bring high winds, heavy rainfall, and storm surges, causing damage to homes, businesses, and infrastructure. Flooding, whether from storm surges or inland river overflows, can lead to extensive water damage and even complete property loss. The sheer volume of claims filed after a major hurricane or flood can overwhelm insurance companies, leading to delays in processing and payouts. The cost of rebuilding and repairing damaged properties often exceeds the initial insurance coverage, leaving many homeowners with substantial out-of-pocket expenses. For example, Hurricane Sandy in 2012 resulted in billions of dollars in insurance claims in New Jersey, highlighting the catastrophic potential of these events.
Risk Assessment and Management by Insurance Companies
Insurance companies utilize sophisticated risk assessment models to determine the likelihood and potential severity of natural disasters in specific areas. These models consider factors such as historical weather data, geographical location, proximity to coastlines and floodplains, and building codes. Based on these assessments, insurers determine premiums, coverage limits, and even decide whether to offer insurance in high-risk areas. Risk management strategies include implementing stricter building codes, encouraging mitigation measures like floodproofing, and utilizing advanced technologies for early warning systems and damage assessment. They also actively re-evaluate policies and premiums based on evolving climate patterns and predictions of increased frequency and intensity of natural disasters.
Natural Disaster Insurance Policies in New Jersey
Several types of insurance policies in New Jersey specifically address damages from natural disasters. Flood insurance, often provided through the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP), is crucial for homeowners in flood-prone areas. While NFIP coverage has limits, it provides crucial financial protection against significant flood-related damage. Comprehensive homeowners insurance policies typically cover damage from wind and hail associated with hurricanes, but flood coverage is usually a separate add-on. Furthermore, some insurers offer supplemental coverage for specific perils, like earthquake insurance, which might be necessary depending on the specific risk factors of a location. It’s important to note that standard homeowners’ insurance policies usually exclude coverage for certain events, like gradual erosion or settling, and specific policy exclusions should be reviewed carefully. Coverage limits vary widely based on the policy, the insured property’s value, and the chosen coverage level. For instance, a homeowner might opt for a higher deductible to lower their premium, but this means a larger out-of-pocket expense in the event of a claim.
Future Trends in New Jersey Insurance
The New Jersey insurance market, like others nationwide, is undergoing significant transformation driven by technological advancements and evolving consumer expectations. These changes are impacting how insurance is offered, priced, and experienced, leading to both opportunities and challenges for insurers and consumers alike. The integration of technology is particularly prominent, reshaping the landscape of risk assessment, claims processing, and customer service.
The increasing adoption of telematics and artificial intelligence (AI) is fundamentally altering the insurance industry in New Jersey. These technologies are not merely supplementary tools but are becoming integral components of core business processes, impacting everything from underwriting to claims management.
Telematics and its Impact on Insurance Premiums and Customer Experience
Telematics, the use of technology to monitor driving behavior, is gaining traction in New Jersey’s auto insurance market. Devices installed in vehicles collect data on driving habits such as speed, acceleration, braking, and mileage. This data allows insurers to create more accurate risk profiles, rewarding safer drivers with lower premiums through usage-based insurance (UBI) programs. For example, a driver consistently demonstrating safe driving habits through telematics data might receive a significant discount compared to a driver with a less favorable driving record. Conversely, drivers with risky driving patterns may see their premiums increase. The increased accuracy in risk assessment leads to fairer premiums based on individual behavior rather than broad demographic categories. From a customer experience perspective, UBI programs offer transparency and the potential for personalized savings, fostering a more engaged and trusting relationship between the insurer and the policyholder. However, concerns about data privacy and the potential for algorithmic bias need careful consideration and appropriate regulatory oversight.
Artificial Intelligence and its Role in Underwriting and Claims Processing
AI is rapidly transforming various aspects of the insurance industry, significantly impacting underwriting and claims processing. AI-powered algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data – from credit scores and driving records to social media activity and even satellite imagery – to assess risk more accurately and efficiently than traditional methods. This leads to faster and more streamlined underwriting processes, potentially reducing the time it takes to obtain insurance coverage. In claims processing, AI can automate tasks like initial damage assessment, fraud detection, and claims settlement, leading to quicker payouts for policyholders. For instance, AI-powered image recognition can quickly assess the damage to a vehicle after an accident, speeding up the claims process and minimizing delays. However, the implementation of AI also raises concerns regarding algorithmic bias and the potential displacement of human workers. Insurers need to ensure fairness and transparency in their AI systems and invest in retraining programs for employees whose roles might be affected by automation.
Future Insurance Product Diversification
The convergence of telematics and AI is expected to lead to a diversification of insurance products. We can anticipate the emergence of more personalized and granular insurance offerings tailored to individual risk profiles. For example, insurers might offer customized auto insurance policies based on specific driving behaviors or even create insurance products that cover emerging risks associated with autonomous vehicles or drone technology. Furthermore, the use of AI and predictive modeling could enable insurers to offer more proactive risk management services, such as alerts for potential hazards or recommendations for preventative measures. This shift towards personalized and preventative insurance solutions will transform the customer experience, moving away from a reactive model to a more proactive and consultative approach.
Conclusive Thoughts
The New Jersey insurance market, while complex, offers a wide array of options to meet diverse needs. By understanding the key players, the types of coverage available, and the regulatory framework in place, residents and businesses can navigate the process with greater confidence. Remember to carefully compare policies, consider your individual risk factors, and utilize available resources to ensure you have the appropriate level of protection. Proactive engagement with your insurer and awareness of your rights as a consumer are vital for a positive insurance experience in New Jersey.
Expert Answers
What is the role of the New Jersey Department of Banking and Insurance (DOBI)?
The DOBI regulates the insurance industry in New Jersey, ensuring fair practices, protecting consumers, and maintaining the solvency of insurance companies. They license insurers, investigate complaints, and enforce state insurance laws.
How can I file a complaint against an insurance company in New Jersey?
You can file a complaint with the DOBI through their website or by contacting them directly. They provide resources and assistance to resolve disputes between consumers and insurers.
What factors affect the cost of car insurance in New Jersey besides driving history and location?
Several factors influence car insurance premiums, including age, credit score, the type of vehicle, and the coverage levels chosen. Discounts for safety features, good student status, and multiple policies with the same insurer are also common.
Are flood insurance and homeowners insurance the same thing in New Jersey?
No. Homeowners insurance typically does *not* cover flood damage. Flood insurance is usually purchased separately through the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) or a private insurer.