
Securing affordable and comprehensive health insurance can feel like navigating a complex maze, especially within the unique landscape of the Texas medical insurance marketplace. This guide offers a clear path, unraveling the intricacies of plan selection, eligibility requirements, and financial assistance programs available to Texans. We’ll explore the roles of both federal and state governments in shaping this marketplace, examining the various plan types and their associated costs. Understanding these aspects empowers individuals and families to make informed decisions about their healthcare coverage.
From understanding the Affordable Care Act’s impact on Texas to addressing common challenges and opportunities within the system, this guide provides a holistic overview. We’ll delve into practical steps for enrollment, utilizing the online marketplace resources effectively, and comparing different plan options to find the best fit for individual needs and budgets. Real-world examples and frequently asked questions will further illuminate the process, making healthcare access in Texas more manageable and less daunting.
Overview of the Texas Medical Insurance Marketplace

The Texas medical insurance marketplace, officially part of the federal Health Insurance Marketplace, offers Texans a platform to compare and purchase health insurance plans that meet the requirements of the Affordable Care Act (ACA). Unlike some states, Texas does not operate its own state-based marketplace. This means the federal government plays a more significant role in managing and regulating the marketplace within the state.
The marketplace functions as a central hub where individuals and families can explore various health insurance options from different private insurance providers. The system is designed to be user-friendly, allowing consumers to filter plans based on factors like cost, coverage, and network of doctors and hospitals. The ultimate goal is to provide Texans with a transparent and accessible way to find affordable and comprehensive health insurance.
The Roles of Federal and State Governments
The federal government, through the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), is primarily responsible for the operation and oversight of the Texas Health Insurance Marketplace. This includes establishing the eligibility requirements, setting the standards for plan offerings, and ensuring compliance with federal regulations. The state government, while not directly administering the marketplace, plays a supporting role in outreach and education efforts, often partnering with local organizations to inform Texans about their options. State regulations may also indirectly impact the marketplace through related healthcare laws and policies, although the core regulatory framework remains federally driven.
Types of Health Insurance Plans Available
The Texas Health Insurance Marketplace offers a range of health insurance plans, categorized primarily by their level of coverage and cost. These generally include:
- Bronze Plans: These plans have the lowest monthly premiums but also the highest out-of-pocket costs. They cover a smaller percentage of medical expenses than other plans.
- Silver Plans: Silver plans offer a balance between premium costs and out-of-pocket expenses. They represent a middle ground in terms of cost-sharing compared to Bronze and Gold plans.
- Gold Plans: Gold plans have higher monthly premiums than Silver plans but lower out-of-pocket maximums. This means lower cost-sharing responsibility for the insured.
- Platinum Plans: These plans have the highest monthly premiums but the lowest out-of-pocket costs. They cover a significantly larger percentage of medical expenses than other plans.
- Catastrophic Plans: Available to individuals under 30 or those with a hardship exemption, these plans have very low monthly premiums but high deductibles and out-of-pocket maximums. They primarily cover catastrophic illnesses or injuries.
It’s important to note that specific plan details, including provider networks and covered services, vary by insurance company and plan type. Consumers should carefully review the details of each plan before making a selection.
Eligibility and Enrollment in the Texas Marketplace
Navigating the Texas Medical Insurance Marketplace can seem daunting, but understanding the eligibility requirements and enrollment process simplifies the experience. This section provides a clear guide to help Texans find affordable healthcare coverage.
Eligibility for marketplace plans depends on several factors, primarily income and residency. The marketplace offers subsidized plans to individuals and families whose income falls within certain limits. Residency in Texas is, of course, a fundamental requirement. Beyond these basic criteria, other factors, such as citizenship status and immigration documentation, may also play a role in determining eligibility.
Determining Eligibility for Marketplace Plans
To determine your eligibility, you’ll need to gather some key information. This includes your household income, the number of people in your household, and your citizenship or immigration status. You can then use the HealthCare.gov website or contact the marketplace directly to determine if you qualify for financial assistance or subsidized plans. A step-by-step process is detailed below.
- Gather Necessary Information: Collect details on your household income (including all sources), the number of people in your household, and your citizenship or immigration status. If applicable, gather information regarding any current employer-sponsored health insurance coverage.
- Visit HealthCare.gov or Contact the Marketplace: Use the online tools at HealthCare.gov to estimate your eligibility or contact the marketplace directly via phone or email for personalized assistance. The website provides income-based eligibility calculators and other resources to aid in the process.
- Review Eligibility Determination: Carefully review the eligibility determination provided by the marketplace. If you disagree with the determination, you can usually appeal the decision within a specific timeframe.
- Verify Information: Double-check all provided information to ensure accuracy. Inaccurate information can delay or prevent enrollment.
Enrollment Period and Process
The annual Open Enrollment Period (OEP) for the Texas Marketplace typically runs for a few months in the fall. During this period, individuals can enroll in or change their health insurance plans. Outside of the OEP, there are limited circumstances where you can enroll, such as experiencing a qualifying life event (e.g., marriage, birth of a child, loss of other coverage).
The enrollment process is generally straightforward. Once eligibility is determined, you can browse available plans based on your needs and budget. This typically involves comparing plans based on premiums, deductibles, co-pays, and network of providers. After selecting a plan, you’ll need to provide necessary information and complete the enrollment application.
Financial Assistance Programs
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) provides substantial financial assistance to eligible individuals and families to make health insurance more affordable. This assistance can significantly reduce monthly premiums and out-of-pocket costs. The amount of financial assistance you receive is based on your income and household size. Subsidies are available in the form of tax credits that lower your monthly premiums and cost-sharing reductions that reduce your out-of-pocket expenses like deductibles and co-pays.
Enrollment Process Flowchart
Imagine a flowchart with the following steps:
Start –> Determine Eligibility (Gather Information, Use Online Tools/Contact Marketplace) –> Eligible? (Yes/No) –> Yes: Select Plan, Complete Application, Enroll –> No: Explore Other Options, Appeal Decision (if applicable) –> End
The flowchart visually represents the decision points and actions involved in the enrollment process. The ‘Eligible?’ decision point branches into two paths, one for those who qualify and one for those who don’t. Those who don’t qualify might explore alternative options or appeal the eligibility decision.
Plan Options and Costs
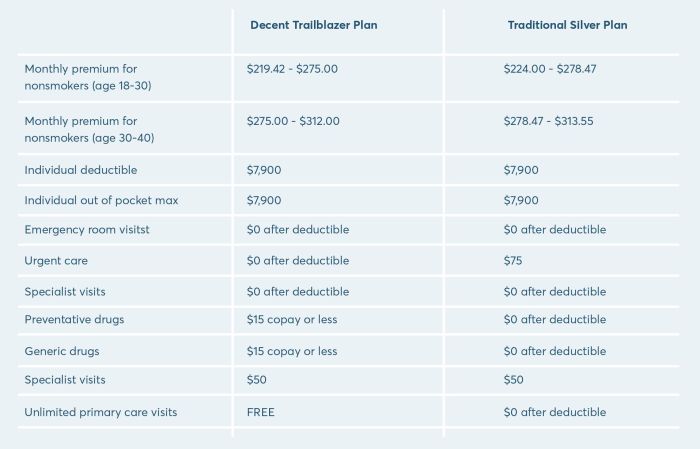
Choosing a health insurance plan can feel overwhelming, given the variety of options and associated costs. Understanding the different plan types and the factors influencing their price is crucial for making an informed decision on the Texas marketplace. This section will clarify the key aspects of plan options and their respective costs.
Health Insurance Plan Types
The Texas marketplace offers several types of health insurance plans, each with its own structure and cost implications. The most common types are HMOs, PPOs, and EPOs. Understanding their differences is essential for selecting a plan that best suits your healthcare needs and budget.
HMO (Health Maintenance Organization): HMO plans typically require you to choose a primary care physician (PCP) within the plan’s network. Referrals from your PCP are usually needed to see specialists. Generally, HMO plans offer lower premiums but may have stricter limitations on accessing out-of-network care. They often emphasize preventative care.
PPO (Preferred Provider Organization): PPO plans offer more flexibility. You can generally see any doctor or specialist, in-network or out-of-network, without needing a referral. However, seeing out-of-network providers will result in higher costs. PPO plans usually have higher premiums than HMOs but offer greater choice and convenience.
EPO (Exclusive Provider Organization): EPO plans are a hybrid of HMOs and PPOs. Like HMOs, they typically require you to choose a PCP within the network. Unlike HMOs, however, they may allow you to see specialists without a referral, but only within the network. Seeing out-of-network providers is generally not covered.
Factors Influencing Health Insurance Costs
Several factors influence the cost of your health insurance plan. These include:
Age: Generally, older individuals tend to pay higher premiums than younger individuals because they statistically utilize more healthcare services. This is a common actuarial principle used by insurance companies to assess risk.
Location: The cost of healthcare varies geographically. Plans in areas with higher healthcare costs, such as major metropolitan areas, typically have higher premiums than those in more rural areas. This reflects the higher cost of medical services and provider fees in those regions.
Health Status: Individuals with pre-existing conditions or a history of significant healthcare utilization may face higher premiums. Insurance companies assess risk based on this information. However, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) prohibits insurers from denying coverage or charging higher premiums solely based on pre-existing conditions.
Sample Plan Cost Comparison
The following table provides a simplified comparison of potential premium costs, deductibles, and co-pays for different plan types. Remember that actual costs vary significantly based on the specific plan, location, age, and other factors. These figures are illustrative examples only and should not be considered definitive.
| Plan Type | Monthly Premium (Estimate) | Annual Deductible (Estimate) | Co-pay (Doctor Visit, Estimate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HMO | $300 | $1,500 | $25 |
| PPO | $450 | $3,000 | $50 |
| EPO | $350 | $2,000 | $35 |
Navigating the Marketplace Website and Resources
The Texas Medical Insurance Marketplace website is designed to be user-friendly, guiding individuals through the process of selecting a health insurance plan that meets their needs and budget. Understanding its features and available resources is key to a successful enrollment experience. This section provides a practical guide to navigating the site and accessing support.
The website’s primary function is to allow Texans to browse and compare health insurance plans offered by various providers. This comparison is based on factors such as premiums, deductibles, co-pays, and network of doctors and hospitals. The site also provides tools to estimate costs and determine eligibility for financial assistance, like subsidies.
Website Navigation and Plan Comparison
The Texas Marketplace website typically features a clear and intuitive layout. Users will usually find a prominent search bar allowing for quick searches based on zip code or plan specifics. Navigation menus usually organize information into categories such as “Find a Plan,” “Learn About Plans,” and “Enroll.” Within the “Find a Plan” section, users can filter plans based on their preferences (e.g., price range, provider network, plan type – HMO, PPO, etc.). The site usually displays plans in a table format, allowing side-by-side comparison of key features and costs. Detailed plan information, including provider directories and benefit summaries, is usually accessible with a single click. For example, a user could search for plans in Austin, Texas, specifying a maximum monthly premium and a preference for a specific network of doctors. The site would then display a list of plans matching these criteria, allowing for a direct comparison.
Customer Support Resources
The Texas Marketplace provides various customer support channels to assist users throughout the enrollment process. These usually include a frequently asked questions (FAQ) section addressing common queries. Contact information for phone support and email inquiries is also typically readily available. In some cases, live chat support may be offered during peak enrollment periods. Additionally, the site may link to external resources such as navigator programs offering in-person assistance. For instance, a user struggling to understand the difference between an HMO and a PPO can consult the FAQ section or contact customer support via phone or email for clarification.
Using the Website’s Tools
The website incorporates several tools designed to simplify the plan selection process. A plan comparison tool allows users to select multiple plans and compare them side-by-side based on key metrics. A cost estimator helps users predict their out-of-pocket expenses based on their expected healthcare utilization. Eligibility tools determine if users qualify for subsidies or other financial assistance programs. These tools are typically accessed through clearly labeled buttons or links within the website’s main navigation. For example, a user can use the cost estimator to input their anticipated medical expenses for the year and receive an estimate of their total cost under different plan options. This allows for informed decision-making.
Impact of Healthcare Reform on the Texas Marketplace
The Affordable Care Act (ACA), also known as Obamacare, significantly reshaped the Texas healthcare landscape, impacting both the availability and affordability of health insurance. While its implementation faced political challenges in Texas, its effects on the state’s medical insurance marketplace are undeniable and continue to evolve. This section examines the ACA’s influence on plan options, affordability, and enrollment trends within the Texas marketplace.
The ACA’s expansion of Medicaid eligibility, although not fully adopted by Texas, created a ripple effect across the state’s insurance market. The law mandated that insurers offer a defined set of essential health benefits, prohibiting exclusions for pre-existing conditions and guaranteeing access to preventative care. This resulted in a shift in the types of plans available and influenced their pricing structures.
Changes in Plan Availability and Affordability
The ACA’s impact on plan availability in Texas is complex. While the mandate for essential health benefits broadened coverage, it also led to some insurers withdrawing from the marketplace, particularly in certain rural areas, due to perceived financial risks associated with covering a wider range of individuals with higher healthcare needs. This resulted in a reduction in the number of insurers offering plans in some regions, leading to less choice for consumers in those areas. Conversely, the increased availability of subsidies and tax credits under the ACA made health insurance more affordable for many Texans, especially those with lower incomes. The impact of these subsidies varied depending on income level and plan selection, but they demonstrably increased access to coverage for a significant portion of the population. A study by the Kaiser Family Foundation, for example, showed a considerable reduction in the uninsured rate in Texas following the ACA’s implementation, though the rate remains higher than the national average.
Enrollment Trends and Changes in the Insured Population
Since the ACA’s implementation, Texas has seen a noticeable increase in its insured population, although the growth has been less dramatic than in states that expanded Medicaid. Data from the U.S. Census Bureau and the Texas Health and Human Services Commission illustrate a decrease in the uninsured rate. However, significant disparities remain, with uninsured rates considerably higher among specific demographics, such as Hispanic Texans and those residing in rural communities. The annual open enrollment periods under the ACA have also demonstrated fluctuations in enrollment numbers, influenced by factors such as economic conditions, outreach efforts, and changes in federal policy. These fluctuations highlight the ongoing need for effective strategies to increase awareness and access to affordable healthcare coverage among the Texas population. Further analysis of this data reveals that while the ACA expanded access to insurance, persistent challenges in affordability and availability remain for some segments of the Texas population.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Texas Marketplace
The Texas medical insurance marketplace, while offering a crucial pathway to affordable healthcare, faces significant hurdles in ensuring equitable access for all residents. These challenges stem from a complex interplay of socioeconomic factors, regulatory landscapes, and the unique characteristics of the Texas healthcare system. Addressing these challenges presents considerable opportunities to improve the marketplace’s efficiency and effectiveness, ultimately leading to better health outcomes for Texans.
The high percentage of uninsured Texans and the state’s relatively low Medicaid expansion rate represent substantial barriers to accessing affordable healthcare. This leads to delayed or forgone care, resulting in poorer health outcomes and increased healthcare costs in the long run. Further complicating matters is the limited availability of providers, particularly in rural areas, coupled with the often-high cost of healthcare services. These factors disproportionately impact low-income individuals and families, creating significant health disparities.
High Uninsurance Rates and Limited Medicaid Expansion
Texas has consistently ranked among the states with the highest rates of uninsured residents. This is largely attributed to the state’s decision not to expand Medicaid eligibility under the Affordable Care Act (ACA). The consequences of this decision are far-reaching, leaving many low-income adults without access to affordable healthcare coverage. This lack of coverage often leads to delayed or forgone preventative care, resulting in more expensive and complex health issues later. For example, individuals without insurance may delay seeking treatment for chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension, leading to severe complications requiring significantly more expensive interventions. The financial burden on uninsured individuals and the overall healthcare system is substantial.
Limited Provider Availability and High Healthcare Costs
Access to healthcare is not solely determined by insurance coverage. The availability of healthcare providers, especially specialists, is unevenly distributed across Texas. Rural communities often face significant shortages, forcing residents to travel long distances for care. Simultaneously, the cost of healthcare services in Texas remains high, making even those with insurance struggle to afford necessary care, particularly for those with high deductibles or co-pays. This disparity in access and affordability contributes to significant health inequities across the state.
Opportunities for Improvement
Improving the Texas medical insurance marketplace requires a multifaceted approach. Expanding Medicaid eligibility would significantly reduce the number of uninsured Texans, providing access to preventative care and early intervention, thereby reducing long-term healthcare costs. Furthermore, incentivizing healthcare providers to practice in underserved areas, such as offering loan forgiveness programs or tax breaks, would help address the provider shortage. Finally, implementing measures to control healthcare costs, such as negotiating lower drug prices or promoting greater transparency in pricing, would make healthcare more affordable for all Texans. These initiatives would collectively enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the marketplace, leading to better health outcomes and reduced healthcare disparities.
Illustrative Example: A Texas Family’s Experience
The Hernandez family, residing in Austin, Texas, faced a significant challenge when their previous employer-sponsored health insurance ended. With three children, ages 8, 12, and 15, and Mr. Hernandez recently self-employed, securing affordable and comprehensive healthcare became a top priority. Their experience navigating the Texas Medical Insurance Marketplace offers a valuable case study illustrating both the challenges and the potential benefits of the system.
The Hernandez Family’s Situation and Needs
The Hernandez family needed a plan that covered preventative care, routine check-ups, and potential unexpected medical expenses. Their 15-year-old daughter, Sofia, requires regular allergy medication, while their youngest, Miguel, recently needed dental work. Mr. and Mrs. Hernandez both needed general health coverage. Financially, they needed a plan that fit within their budget, considering Mr. Hernandez’s fluctuating income as a freelance graphic designer. They were particularly concerned about out-of-pocket costs like deductibles and co-pays.
Navigating the Marketplace Website and Selecting a Plan
The Hernandez family initially found the Healthcare.gov website somewhat overwhelming. They utilized the marketplace’s built-in assistance tools, including the plan comparison tool and eligibility calculator. These tools helped them understand the various plan options available, including HMOs, PPOs, and EPOs. They carefully considered factors like provider networks, premium costs, deductibles, and co-pays. After several weeks of research and comparison, they chose a Silver-level plan that offered a balance between affordability and comprehensive coverage. This plan included their preferred pediatrician and dentist within its network.
Financial Implications of the Chosen Plan
The chosen Silver plan had a monthly premium of $850. This was significantly less than some of the more comprehensive plans they considered, but still represented a substantial portion of their monthly budget. They were relieved that the plan covered a significant portion of their healthcare costs, reducing their financial risk in case of unexpected medical expenses. While they had a deductible of $5,000, the monthly premium was manageable, and the co-pays were relatively low. The plan’s coverage for Sofia’s allergy medication and Miguel’s dental work significantly reduced their out-of-pocket expenses. They opted for a monthly payment plan to manage the premium payments effectively.
Impact on the Hernandez Family
The Hernandez family’s experience highlights the importance of careful planning and research when selecting a health insurance plan. While the process initially felt daunting, the available resources and tools on the marketplace website ultimately guided them to a suitable plan. Securing affordable and comprehensive health insurance provided them with significant peace of mind, allowing them to focus on their family and Mr. Hernandez’s business without the constant worry of potential medical debt. The plan’s coverage for their children’s healthcare needs was particularly impactful, ensuring they received necessary care without undue financial strain.
Conclusive Thoughts
Successfully navigating the Texas medical insurance marketplace requires careful consideration of individual circumstances and a thorough understanding of the available options. By utilizing the resources Artikeld in this guide, Texans can confidently assess their eligibility, compare plans effectively, and secure the healthcare coverage that best meets their needs and budget. Remember, access to affordable and quality healthcare is a fundamental right, and this guide aims to empower you to exercise that right.
Questions and Answers
What is the open enrollment period for the Texas marketplace?
The open enrollment period for the Affordable Care Act marketplaces typically runs for a limited time each year, usually in the fall. Specific dates are announced annually by the federal government. It’s crucial to check the official Healthcare.gov website for the most up-to-date information.
Can I get help paying for my insurance through the marketplace?
Yes, the marketplace offers financial assistance programs, including tax credits and subsidies, to help lower the cost of health insurance premiums. Eligibility is based on income and household size. The marketplace website provides a tool to determine your eligibility and estimate your potential savings.
What if I have a pre-existing condition?
The Affordable Care Act prohibits health insurance companies from denying coverage or charging higher premiums based on pre-existing conditions. You should be able to find coverage regardless of your health status.
What types of plans are available on the Texas marketplace?
Several types of plans are typically available, including HMOs (Health Maintenance Organizations), PPOs (Preferred Provider Organizations), and EPOs (Exclusive Provider Organizations). Each has different cost-sharing structures and network restrictions. The marketplace website allows you to compare these plans side-by-side.
Where can I find more information and assistance?
The official Healthcare.gov website is a great starting point. You can also contact the marketplace directly through their customer service channels or seek assistance from a certified navigator or enrollment assister in your community.